Immunohistochemical evaluation of hepatic progenitor cells in different types of feline liver diseases
- PMID: 33583913
- PMCID: PMC8111336
- DOI: 10.1292/jvms.20-0435
Immunohistochemical evaluation of hepatic progenitor cells in different types of feline liver diseases
Abstract
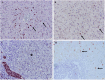
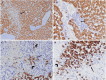
Hepatic progenitor cells are periportally resident cells capable of differentiating into mature hepatocytes or cholangiocytes to ensure hepatic regeneration. This reaction is termed a ductular reaction. In the present study, regenerative response of the feline liver to different hepatic diseases was investigated immunohistochemically. Regeneration of the liver through hepatocellular replication and proliferation of progenitor cell compartment were comparatively evaluated. Histological and immunohistochemical stainings were conducted on feline liver samples (n=40) representing various hepatobiliary diseases. Cytokeratin (CK) 7, CK19, Proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA), Ki67, and Human hepatocyte marker 1 (Hep Par-1) were used. The presence of progenitor cells within feline livers was proved, both as passive cells in normal liver and as active cells (ductular reaction) in hepatic lesions. CK7 was found to be a suitable antibody for immunohistochemically detecting feline progenitor cells. In acute events, regeneration was predominantly shaped by the division of hepatocytes. In chronic events and severe acute events, hepatocytes lost their ability to divide and regeneration mainly occurred through progenitor cells. Location of the ductular reaction varied between different hepatic diseases. Parenchymal ductular reaction was detected in fulminant hepatitis, chronic hepatitis, hepatocellular lipidosis and metastatic lymphoma, whereas septal ductular reaction was detected in chronic hepatitis and metastatic lymphoma. Ductular reaction exhibited positive staining for Hep Par-1 in chronic and severe acute events. This study indicates the major role played by hepatic progenitor cells in regeneration of the feline liver. Moreover, it shows how the activation pattern of ductular reaction varies according to the hepatobiliary disease type.
Keywords: ductular reaction; feline; hepatic progenitor cell; immunohistochemistry; regeneration.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The progenitor cell compartment in the feline liver: an (immuno)histochemical investigation.Vet Pathol. 2009 Jul;46(4):614-21. doi: 10.1354/vp.07-VP-0097-I-FL. Epub 2009 Mar 27. Vet Pathol. 2009. PMID: 19329493
-
Identification of bipotential progenitor cells in human liver regeneration.Lab Invest. 1996 Nov;75(5):699-705. Lab Invest. 1996. PMID: 8941215
-
Ductular proliferation in liver tissues with severe chronic hepatitis B: an immunohistochemical study.World J Gastroenterol. 2006 Mar 7;12(9):1443-6. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i9.1443. World J Gastroenterol. 2006. PMID: 16552818 Free PMC article.
-
[Which stem cells for adult liver?].Ann Pathol. 2005 Feb;25(1):33-44. doi: 10.1016/s0242-6498(05)80097-5. Ann Pathol. 2005. PMID: 15981930 Review. French.
-
Potential of regenerative medicine techniques in canine hepatology.Vet Q. 2013 Dec;33(4):207-16. doi: 10.1080/01652176.2013.875240. Epub 2014 Jan 14. Vet Q. 2013. PMID: 24422896 Review.
Cited by
-
Casein kinase 1 epsilon (CK1ε) as a potential therapeutic target in chronic liver disease.J Vet Sci. 2025 May;26(3):e30. doi: 10.4142/jvs.24321. J Vet Sci. 2025. PMID: 40461423 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ductular reaction in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: When Macbeth is perverted.World J Hepatol. 2023 Jun 27;15(6):725-740. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v15.i6.725. World J Hepatol. 2023. PMID: 37397935 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prognostic role of the stromal cell derived factor-1 in patients with hepatitis B virus-related acute-on-chronic liver failure.World J Clin Cases. 2024 Jul 6;12(19):3845-3853. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i19.3845. World J Clin Cases. 2024. PMID: 38994298 Free PMC article.
-
Features of Ductular Reaction in Rats with Extrahepatic Cholestasis.Bull Exp Biol Med. 2022 Apr;172(6):770-774. doi: 10.1007/s10517-022-05475-6. Epub 2022 May 3. Bull Exp Biol Med. 2022. PMID: 35503585
-
Mechanisms of ductular reaction in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis.World J Gastroenterol. 2022 May 21;28(19):2088-2099. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i19.2088. World J Gastroenterol. 2022. PMID: 35664038 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Cullen J. M., Stalker M. J.2016. Liver and Biliary System. pp. 259–351. In: Jubb, Kennedy, and Palmer’s Pathology of Domestic Animals, 6th ed. (Grant Maxie, M. ed.), Elsevier, Philadelphia.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

