Management of Large Oroantral Fistulas Caused by Medication-Related Osteonecrosis with the Combined Sequestrectomy, Buccal Fat Pad Flap and Platelet-Rich Fibrin
- PMID: 33584046
- PMCID: PMC7855103
- DOI: 10.1007/s12663-019-01278-x
Management of Large Oroantral Fistulas Caused by Medication-Related Osteonecrosis with the Combined Sequestrectomy, Buccal Fat Pad Flap and Platelet-Rich Fibrin
Abstract
Purpose: The aim of this retrospective study was to describe the efficacy of management of bisphosphonate-related maxillary osteonecrosis, which had resulted in an oroantral fistula formation, by performing sequestrectomy, platelet-rich fibrin (PRF) and buccal fat pad (BFP) flap.
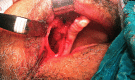
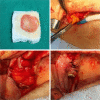
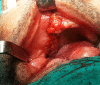
Patient and methods: A total of 7 patients diagnosed with stage III maxillary medication-related osteonecrosis according to guidelines of the American Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons. All patients complained of persistent pain, swelling and purulent drainage with sinusitis. In order to keep the infection under control, the patients first received an antibiotic combination for 2 weeks. Then, sequestrectomy and bone debridement were performed under general anesthesia. After that, an antrectomy was performed via endoscopic sinus surgery in some cases. And the fistula was closed with BFP after or before the PRF application to the region depending on the size of the fistula.
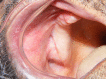
Results: The fistula was successfully closed. After a mean follow-up of 16 months, no symptoms were seen in the patients.
Conclusions: The patients were successfully managed with a combined treatment consisted of sequestrectomy, PRF and BFP. We suggest that large defects arose from medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw can be managed with such a combined approach in order to lessen the recurrence risk.
Keywords: Bisphosphonates; Buccal fat pad; Medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw; Oroantral fistula; Platelet-rich fibrin; Sequestrectomy.
© The Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons of India 2019.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Ruggiero SL, Dodson TB, Fantasia J, Goodday R, Agbaloo T, Mebrotra B, O’Ryan F. American Association of oral and maxillofacial surgeons position paper on medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw—2014 update. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2014;72(10):1938–1956. doi: 10.1016/j.joms.2014.04.031. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bamias A, Kastritis E, Bamia C, Moulopoulos LA, Melakopoulos I, Bozas G, Koutsoukou V, Gika D, Anagnostopoulos A, Papadimitriou C, Terpos E, Dimopoulos M. Osteonecrosis of the jaw in cancer after treatment with bisphosphonates: incidence and risk factors. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23(34):8580–8587. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2005.02.8670. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Mast G, Otto S, Mucke T, Schreyer C, Bissinger O, Kolk A, Wolff KD, Ehrenfeld M, Stürzenbaum SR, Pautke C. Incidence of maxillary sinusitis and oro-antral fistulae in bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis of the jaw. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2012;40(7):568–571. doi: 10.1016/j.jcms.2011.10.012. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
