In silico Molecular Docking, DFT Analysis and ADMET Studies of Carbazole Alkaloid and Coumarins from Roots of Clausena anisata: A Potent Inhibitor for Quorum Sensing
- PMID: 33584098
- PMCID: PMC7875078
- DOI: 10.2147/AABC.S290912
In silico Molecular Docking, DFT Analysis and ADMET Studies of Carbazole Alkaloid and Coumarins from Roots of Clausena anisata: A Potent Inhibitor for Quorum Sensing
Abstract
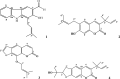
Introduction: In modern drug design, in silico methods are largely used to understand drug-receptor interactions and quantum chemical properties. In the present study, a computational de novo design approach was used to confirm mode of binding for antibacterial activity, elucidating quantum chemical properties and ADMET-drug-likeness of carbazole alkaloid (1) and three coumarins (2-4) isolated from roots of Clausena anisata.
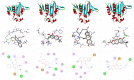
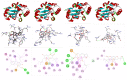
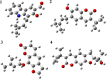
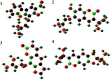
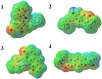
Methods: Docking studies were performed with DNA-Gyrase (6F86) and LasR binding domain (2UV0) employing a flexible ligand docking approach using AutoDock Vina. SwissADME prediction and toxicological predictions were performed by ADMET. The optimized structures and molecular electrostatic potential surface of the isolated compounds were predicted by DFT analysis using B3LYP/6-31G basis levels.
Results and discussion: The docking results revealed that compound 3 showed better docking scores against both DNA gyrase B and LasR binding domain compared with ciprofloxacin with potential as an inhibitor of bacterial DNA gyrase and quorum sensing LasR binding domain. The SwissADME prediction results showed that all the isolated compounds (1-4) satisfy Lipinski's rule of five with zero violations. Toxicological prediction results suggested that all compounds and ciprofloxacin are non-hepatotoxic, non-carcinogenic, non-irritant, immunogenic, and non-cytotoxic. The DFT analysis results revealed that compound 3 has large electronegativity (χeV), global softness (σ eV-1), global electrophilicity (ωeV), and mutagenicity value closer to ciprofloxacin (with LD50 value of 480 mg/kg) suggesting better bioactivity and chemical reactivity with considerable intra-molecular charge transfer between electron-donor to electron-acceptor groups.
Conclusion: Overall, compound 3 may serve as a lead molecule that could be developed into a potent E. coli DNA gyrase B inhibitor and efficient inhibitor for quorum sensing auto-inducer LasR binding domain of Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
Keywords: DNA gyrase; LasR binding domain; alkaloids; coumarins; de novo DFT and docking studies.
© 2021 Eswaramoorthy et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

