Cynandione A Alleviates Neuropathic Pain Through α7-nAChR-Dependent IL-10/β-Endorphin Signaling Complexes
- PMID: 33584292
- PMCID: PMC7873367
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2020.614450
Cynandione A Alleviates Neuropathic Pain Through α7-nAChR-Dependent IL-10/β-Endorphin Signaling Complexes
Abstract
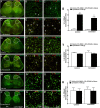
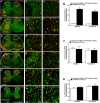
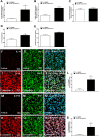
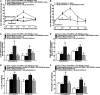
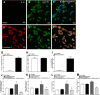
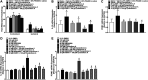
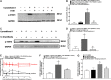
Cynandione A, an acetophenone isolated from Cynanchum Wilfordii Radix, exhibits antineuropathic pain effect. This study further explored the target molecule and signaling mechanisms underlying cynandione-A-induced antineuropathic pain. Intrathecal injection of cynandione A significantly attenuated mechanical allodynia in neuropathic rats and substantially increased spinal expression of IL-10 and β-endorphin but not dynorphin A. Cynandione A treatment also enhanced expression of IL-10 and β-endorphin but not α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs) in cultured microglia. The IL-10 antibody attenuated cynandione-A-induced spinal or microglial gene expression of β-endorphin and mechanical allodynia, whereas the β-endorphin antiserum blocked cynandione-A-induced mechanical antiallodynia but not spinal or microglial IL-10 gene expression. The α7 nAChR antagonist methyllycaconitine significantly reduced cynandione-A-induced mechanical antiallodynia and spinal or microglial expression of IL-10 and β-endorphin. Furthermore, cynandione A stimulated microglial phosphorylation of PKA, p38, and CREB in an α7-nAChR-dependent manner, and treatment with their inhibitors attenuated cynandione-A-induced mechanical antiallodynia and spinal or microglial expression of IL-10 and β-endorphin. In addition, cynandione A stimulated spinal phosphorylation of the transcription factor STAT3, which was inhibited by methyllycaconitine, the PKA activation inhibitor or IL-10 antibody. The STAT3 inhibitor NSC74859 also abolished cynandione-A-induced mechanical antiallodynia and spinal expression of β-endorphin. These findings suggest that cynandione A suppresses neuropathic pain through α7-nAChR-dependent IL-10/β-endorphin signaling pathway in spinal microglia.
Keywords: cynandione A; interleukin-10; microglia; neuropathic pain; α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor; β-endorphin.
Copyright © 2021 Han, Yin, Wang, Liu, Ao and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Apryani E., Ali U., Wang Z. Y., Wu H. Y., Mao X. F., Ahmad K. A., et al. (2020). The spinal microglial IL-10/β-endorphin pathway accounts for cinobufagin-induced mechanical antiallodynia in bone cancer pain following activation of α7-nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. J. Neuroinflammation 17 (1), 75 10.1186/s12974-019-1616-z - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Arredondo J., Chernyavsky A. I., Jolkovsky D. L., Pinkerton K. E., Grando S. A. (2006). Receptor-mediated tobacco toxicity: cooperation of the Ras/Raf-1/MEK1/ERK and JAK-2/STAT-3 pathways downstream of alpha7 nicotinic receptor in oral keratinocyte. Faseb. J. 20 (12), 2093–2101. 10.1096/fj.06-6191com - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

