Onabotulinumtoxin A Improves Psychological Aspects in Chronic Migraine Patients
- PMID: 33584525
- PMCID: PMC7873558
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2020.633355
Onabotulinumtoxin A Improves Psychological Aspects in Chronic Migraine Patients
Abstract
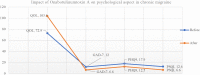
Background: Chronic migraine (CM) affects 5.4% of the Kuwaiti population. It is associated with significant headache-related disability, psychiatric comorbidity and reduced quality of life. The aim of this study is to assess the efficacy of Onabotulinumtoxin A on psychological aspects of chronic migraine patients. Methods: This prospective study over 36 months included chronic migraine patients in a tertiary headache center. Eligible patients met International Classification of Headache Disorders disorders-third edition, beta version (ICHD-III) revision criteria for chronic migraine. Patients with history of psychiatric or medical problems other than migraine disorders were excluded. Patients who received less than 4 injections cycles of Onabotulinumtoxin A were excluded. Identified patients received 155 units of Onabotulinumtoxin A quarterly according to the Phase III Research Evaluating Migraine Prophylaxis Therapy Trail (PREEMPT) protocol. Quality of life, the seven-item Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD-7) scores, the nine-item Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ9), and the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (PSQI) were collected before injection and at the end of the study. Mean comparison tests were performed using the independent sample t-test to assess the effects of Onabotulinumtoxin A on quality of life and comorbid symptoms of anxiety, depression, and quality of sleep. Results: The study identified 131 chronic migraine patients with a mean age of 44.92 years, mean disease duration of 12.20 years and a mean treatment sessions of 7.58. In their last visit, most of our sample showed improvement in quality of life (81%), GAD-7 (81%), PHQ9 (79%), and PSQ1 (76%). The mean score of patient satisfaction was 7.21. Onabotulinumtoxin A treatment for CM improved quality of life significantly (72.92 vs. 103.62; P < 0.0001). It was also associated with significant reduction in anxiety [GAD-7 (12.00 vs. 6.61; P < 0.0001)] and depression [PHQ-9 (17.91 vs. 12.52; P < 0.0001)] scores, as well as reduced difficulty in sleeping [PSQI (12.60 vs. 6.66; P < 0.0001)] at the last visit. Conclusion: Prophylactic Onabotulinumtoxin A treatment for CM was associated with significant improvement of quality of life, reduction in symptoms of anxiety and depression, as well as improved symptoms of poor sleep.
Keywords: Onabotulinumtoxin A; anxiety; chronic migraine; depression; sleep disturbance.
Copyright © 2021 Al-Hashel, Kh Ashkanani, Almutairi, Bokubar, Mubarak, Alwazzan, Alroughani, Youssry and Farouk Ahmed.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Stovner LJ, Nichols E, Steiner TJ, Abd-Allah F, Abdelalim A, Al-Raddadi RM, et al. Global, regional, and national burden of migraine and tension-type headache, 1990-2016: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet Neurol. (2018) 17:954–76. 10.1016/S1474-4422(18)30322-3 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- (IHME), I. F. H. M. A. E Findings from the Global Burden of Disease Study. Seattle, WA: Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation; (2017).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous