A Virulence Associated Siderophore Importer Reduces Antimicrobial Susceptibility of Klebsiella pneumoniae
- PMID: 33584611
- PMCID: PMC7876324
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.607512
A Virulence Associated Siderophore Importer Reduces Antimicrobial Susceptibility of Klebsiella pneumoniae
Abstract
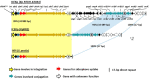
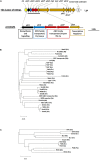
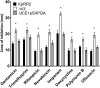
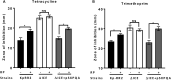
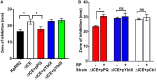
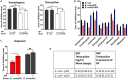
The accessory genomes of many pathogenic bacteria include ABC transporters that scavenge metal by siderophore uptake and ABC transporters that contribute to antimicrobial resistance by multidrug efflux. There are mechanistic and recently recognized structural similarities between siderophore importer proteins and efflux pumps. Here we investigated the influence of siderophore importer YbtPQ on antimicrobial resistance of Klebsiella pneumoniae. YbtPQ is encoded in the yersiniabactin cluster in a prevalent mobile genetic element ICEKp, and is also common in pathogenicity islands of Escherichia coli and Yersinia species, where yersiniabactin enhances virulence. Deletion of ICEKp increased the susceptibility of K. pneumoniae to all antimicrobials tested. The mechanism was dependent on the yersiniabactin importer YbtPQ and may involve antimicrobial efflux, since it was affected by the inhibitor reserpine. The element ICEKp is naturally highly mobile, indeed the accessory genome of K. pneumoniae is recognized as a reservoir of genes for the emergence of hospital outbreak strains and for transfer to other Gram-negative pathogens. Introduction of ICEKp, or a plasmid encoding YbtPQ, to E. coli decreased its susceptibility to a broad range of antimicrobials. Thus a confirmed siderophore importer, on a rapidly evolving and highly mobile element capable of interspecies transfer, may have a secondary function exporting antimicrobials.
Keywords: ABC transporter; Klebsiella pneumoniae; antimicrobial efflux; integrative conjugative element; mobile genetic element; siderophore; yersiniabactin.
Copyright © 2021 Farzand, Rajakumar, Barer, Freestone, Mukamolova, Oggioni and O’Hare.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Genetic diversity, mobilisation and spread of the yersiniabactin-encoding mobile element ICEKp in Klebsiella pneumoniae populations.Microb Genom. 2018 Sep;4(9):e000196. doi: 10.1099/mgen.0.000196. Epub 2018 Jul 9. Microb Genom. 2018. PMID: 29985125 Free PMC article.
-
Pathogenic siderophore ABC importer YbtPQ adopts a surprising fold of exporter.Sci Adv. 2020 Feb 5;6(6):eaay7997. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aay7997. eCollection 2020 Feb. Sci Adv. 2020. PMID: 32076651 Free PMC article.
-
The Yersinia high-pathogenicity island (HPI) carried by a new integrative and conjugative element (ICE) in a multidrug-resistant and hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae strain SCsl1.Vet Microbiol. 2019 Dec;239:108481. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2019.108481. Epub 2019 Oct 31. Vet Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31767086
-
Klebsiella pneumoniae and Klebsiella quasipneumoniae define the population structure of blaKPC-2Klebsiella: a 5 year retrospective genomic study in Singapore.J Antimicrob Chemother. 2019 Nov 1;74(11):3205-3210. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkz332. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2019. PMID: 31504571
-
Characterizing Mobilized Virulence Factors and Multidrug Resistance Genes in Carbapenemase-Producing Klebsiella pneumoniae in a Sri Lankan Hospital.Front Microbiol. 2018 Aug 31;9:2044. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.02044. eCollection 2018. Front Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 30233529 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The Integrative Conjugative Element ICESpyM92 Contributes to Pathogenicity of Emergent Antimicrobial-Resistant emm92 Group A Streptococcus.Infect Immun. 2022 Aug 18;90(8):e0008022. doi: 10.1128/iai.00080-22. Epub 2022 Aug 1. Infect Immun. 2022. PMID: 35913172 Free PMC article.
-
The Microbiological Characteristics and Genomic Surveillance of Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae Isolated from Clinical Samples.Microorganisms. 2025 Jul 4;13(7):1577. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms13071577. Microorganisms. 2025. PMID: 40732086 Free PMC article.
-
Correlation Between Antimicrobial Resistance, Virulence Determinants and Biofilm Formation Ability Among Extraintestinal Pathogenic Escherichia coli Strains Isolated in Catalonia, Spain.Front Microbiol. 2022 Jan 11;12:803862. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.803862. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35087504 Free PMC article.
-
Occurrence of Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria Resulting from the Selective Pressure of Antibiotics: A Comprehensive Analysis of ESBL K. pneumoniae and MRSP Isolated in a Dog with Rhinorrhea.Vet Sci. 2023 May 2;10(5):326. doi: 10.3390/vetsci10050326. Vet Sci. 2023. PMID: 37235409 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive analysis of the microbiome and metabolome in pus from pyogenic liver abscess patients with and without diabetes mellitus.Front Microbiol. 2023 Jun 23;14:1211835. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1211835. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37426007 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bi D., Jiang X., Sheng Z. K., Ngmenterebo D., Tai C., Wang M., et al. (2015). Mapping the resistance-associated mobilome of a carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae strain reveals insights into factors shaping these regions and facilitates generation of a ‘resistance-disarmed’ model organism. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 70 2770–2774. 10.1093/jac/dkv204 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

