Bacterial Quorum-Sensing Systems and Their Role in Intestinal Bacteria-Host Crosstalk
- PMID: 33584614
- PMCID: PMC7876071
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.611413
Bacterial Quorum-Sensing Systems and Their Role in Intestinal Bacteria-Host Crosstalk
Abstract
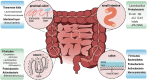
Quorum-sensing (QS) system is a rapidly developing field in which we are gradually expanding our understanding about how bacteria communicate with each other and regulate their activities in bacterial sociality. In addition to collectively modifying bacterial behavior, QS-related autoinducers may also be embedded in the crosstalk between host and parasitic microbes. In this review, we summarize current studies on QS in the intestinal microbiome field and its potential role in maintaining homeostasis under physiological conditions. Additionally, we outline the canonical autoinducers and their related QS signal-response systems by which several pathogens interact with the host under pathological conditions, with the goal of better understanding intestinal bacterial sociality and facilitating novel antimicrobial therapeutic strategies.
Keywords: autoinducers; bacterial communication; host cells; metabolites; quorum sensing.
Copyright © 2021 Wu and Luo.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

