Next Generation Imaging Techniques to Define Immune Topographies in Solid Tumors
- PMID: 33584676
- PMCID: PMC7873485
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.604967
Next Generation Imaging Techniques to Define Immune Topographies in Solid Tumors
Abstract
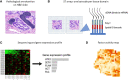
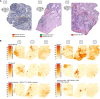
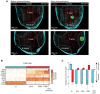
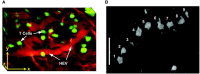
In recent years, cancer immunotherapy experienced remarkable developments and it is nowadays considered a promising therapeutic frontier against many types of cancer, especially hematological malignancies. However, in most types of solid tumors, immunotherapy efficacy is modest, partly because of the limited accessibility of lymphocytes to the tumor core. This immune exclusion is mediated by a variety of physical, functional and dynamic barriers, which play a role in shaping the immune infiltrate in the tumor microenvironment. At present there is no unified and integrated understanding about the role played by different postulated models of immune exclusion in human solid tumors. Systematically mapping immune landscapes or "topographies" in cancers of different histology is of pivotal importance to characterize spatial and temporal distribution of lymphocytes in the tumor microenvironment, providing insights into mechanisms of immune exclusion. Spatially mapping immune cells also provides quantitative information, which could be informative in clinical settings, for example for the discovery of new biomarkers that could guide the design of patient-specific immunotherapies. In this review, we aim to summarize current standard and next generation approaches to define Cancer Immune Topographies based on published studies and propose future perspectives.
Keywords: deep learning; imaging techniques; immune exclusion; immune topography; single-cell analysis; solid tumors.
Copyright © 2021 Pietrobon, Cesano, Marincola and Kather.
Conflict of interest statement
VP and FM were employed by the company Refuge Biotechnologies. AC was employed by ESSA Pharmaceuticals. The remaining author declares that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Brentjens RJ, Rivière I, Park JH, Davila ML, Wang X, Stefanski J, et al. Safety and persistence of adoptively transferred autologous CD19-targeted T cells in patients with relapsed or chemotherapy refractory B-cell leukemias. Blood (2011) 118:4817–28. 10.1182/blood-2011-04-348540 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

