A Glance at the Use of Glucocorticoids in Rare Inflammatory and Autoimmune Diseases: Still an Indispensable Pharmacological Tool?
- PMID: 33584696
- PMCID: PMC7874096
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.613435
A Glance at the Use of Glucocorticoids in Rare Inflammatory and Autoimmune Diseases: Still an Indispensable Pharmacological Tool?
Abstract
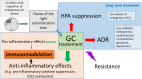
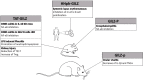
Since their discovery, glucocorticoids (GCs) have been used to treat almost all autoimmune and chronic inflammatory diseases, as well as allergies and some forms of malignancies, because of their immunosuppressive and anti-inflammatory effects. Although GCs provide only symptomatic relief and do not eliminate the cause of the pathology, in the majority of treatments, GCs frequently cannot be replaced by other classes of drugs. Consequently, long-term treatments cause adverse effects that may, in turn, lead to new pathologies that sometimes require the withdrawal of GC therapy. Therefore, thus far, researchers have focused their efforts on molecules that have the same efficacy as that of GCs but cause fewer adverse effects. To this end, some GC-induced proteins, such as glucocorticoid-induced leucine zipper (GILZ), have been used as drugs in mouse models of inflammatory pathologies. In this review, we focus on some important but rare autoimmune and chronic inflammatory diseases for which the biomedical research investment in new therapies is less likely. Additionally, we critically evaluate the possibility of treating such diseases with other drugs, either GC-related or unrelated.
Keywords: autoimmunity; glucocorticoid-induced leucine zipper; glucocorticoids; inflammation; rare disease.
Copyright © 2021 Ronchetti, Ayroldi, Ricci, Gentili, Migliorati and Riccardi.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Caplan A, Fett N, Rosenbach M, Werth VP, Micheletti RG. Prevention and management of glucocorticoid-induced side effects: A comprehensive review: Ocular, cardiovascular, muscular, and psychiatric side effects and issues unique to pediatric patients. J Am Acad Dermatol (2017) 76(2):201–7. 10.1016/j.jaad.2016.02.1241 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

