Cytokines Orchestrating the Natural Killer-Myeloid Cell Crosstalk in the Tumor Microenvironment: Implications for Natural Killer Cell-Based Cancer Immunotherapy
- PMID: 33584718
- PMCID: PMC7878550
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.621225
Cytokines Orchestrating the Natural Killer-Myeloid Cell Crosstalk in the Tumor Microenvironment: Implications for Natural Killer Cell-Based Cancer Immunotherapy
Abstract
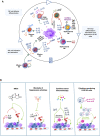
Natural killer (NK) cells are endowed with germline-encoded receptors that enable them to detect and kill malignant cells without prior priming. Over the years, overwhelming evidence has identified an essential role for NK cells in tumor immune surveillance. More recently, clinical trials have also highlighted their potential in therapeutic settings. Yet, data show that NK cells can be dysregulated within the tumor microenvironment (TME), rendering them ineffective in eradicating the cancer cells. This has been attributed to immune suppressive factors, including the tumor cells per se, stromal cells, regulatory T cells, and soluble factors such as reactive oxygen species and cytokines. However, the TME also hosts myeloid cells such as dendritic cells, macrophages, neutrophils, and myeloid-derived suppressor cells that influence NK cell function. Although the NK-myeloid cell crosstalk can promote anti-tumor responses, myeloid cells in the TME often dysregulate NK cells via direct cell-to-cell interactions down-regulating key NK cell receptors, depletion of nutrients and growth factors required for NK cell growth, and secretion of metabolites, chemokines and cytokines that ultimately alter NK cell trafficking, survival, and cytotoxicity. Here, we review the complex functions of myeloid-derived cytokines in both supporting and suppressing NK cells in the TME and how NK cell-derived cytokines can influence myeloid subsets. We discuss challenges related to these interactions in unleashing the full potential of endogenous and adoptively infused NK cells. Finally, we present strategies aiming at improving NK cell-based cancer immunotherapies via pathways that are involved in the NK-myeloid cell crosstalk in the TME.
Keywords: cancer immunotherapy, tumor immunity; cytokines; myeloid cells; natural killer (NK) cells; tumor microenvironment.
Copyright © 2021 Gaggero, Witt, Carlsten and Mitra.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

