Genetic and Epigenetic Consequence of Early-Life Social Stress on Depression: Role of Serotonin-Associated Genes
- PMID: 33584798
- PMCID: PMC7874148
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2020.601868
Genetic and Epigenetic Consequence of Early-Life Social Stress on Depression: Role of Serotonin-Associated Genes
Abstract
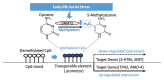
Early-life adversity caused by poor social bonding and deprived maternal care is known to affect mental wellbeing and physical health. It is a form of chronic social stress that persists because of a negative environment, and the consequences are long-lasting on mental health. The presence of social stress during early life can have an epigenetic effect on the body, possibly resulting in many complex mental disorders, including depression in later life. Here, we review the evidence for early-life social stress-induced epigenetic changes that modulate juvenile and adult social behavior (depression and anxiety). This review has a particular emphasis on the interaction between early-life social stress and genetic variation of serotonin associate genes including the serotonin transporter gene (5-HTT; also known as SLC6A4), which are key molecules involved in depression.
Keywords: 5-HT receptor; depression; epigenetic modification; serotonin; social stress.
Copyright © 2021 Soga, Teo and Parhar.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) as a consequence of the interaction between an individual genetic susceptibility, a traumatogenic event and a social context].Encephale. 2012 Oct;38(5):373-80. doi: 10.1016/j.encep.2011.12.003. Epub 2012 Jan 24. Encephale. 2012. PMID: 23062450 Review. French.
-
When the serotonin transporter gene meets adversity: the contribution of animal models to understanding epigenetic mechanisms in affective disorders and resilience.Curr Top Behav Neurosci. 2011;7:251-80. doi: 10.1007/7854_2010_109. Curr Top Behav Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21225411
-
Looking Beyond the 5-HTTLPR Polymorphism: Genetic and Epigenetic Layers of Regulation Affecting the Serotonin Transporter Gene Expression.Mol Neurobiol. 2017 Dec;54(10):8386-8403. doi: 10.1007/s12035-016-0304-6. Epub 2016 Dec 8. Mol Neurobiol. 2017. PMID: 27933583 Review.
-
Unexpected effects of early-life adversity and social enrichment on the anxiety profile of mice varying in serotonin transporter genotype.Behav Brain Res. 2013 Jun 15;247:248-58. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2013.03.039. Epub 2013 Apr 6. Behav Brain Res. 2013. PMID: 23567893
-
Postnatal serotonin type 2 receptor blockade prevents the emergence of anxiety behavior, dysregulated stress-induced immediate early gene responses, and specific transcriptional changes that arise following early life stress.Biol Psychiatry. 2011 Dec 1;70(11):1024-32. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2011.08.005. Epub 2011 Sep 28. Biol Psychiatry. 2011. PMID: 21959103 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Multi-Omics Characterization of Early- and Adult-Onset Major Depressive Disorder.J Pers Med. 2022 Mar 6;12(3):412. doi: 10.3390/jpm12030412. J Pers Med. 2022. PMID: 35330412 Free PMC article.
-
Canada's Colonial Genocide of Indigenous Peoples: A Review of the Psychosocial and Neurobiological Processes Linking Trauma and Intergenerational Outcomes.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 May 26;19(11):6455. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19116455. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35682038 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Deciphering Depression: Epigenetic Mechanisms and Treatment Strategies.Biology (Basel). 2024 Aug 20;13(8):638. doi: 10.3390/biology13080638. Biology (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39194576 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Enduring Neurobiological Consequences of Early-Life Stress: Insights from Rodent Behavioral Paradigms.Biomedicines. 2024 Sep 2;12(9):1978. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12091978. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 39335492 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Corin Missense Variants, Blood Pressure, and Hypertension in 11 322 Black Individuals: Insights From REGARDS and the Jackson Heart Study.J Am Heart Assoc. 2022 Jun 21;11(12):e025582. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.121.025582. Epub 2022 Jun 14. J Am Heart Assoc. 2022. PMID: 35699180 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Benedetti F., Radaelli D., Poletti S., Locatelli C., Dallaspezia S., Lorenzi C., et al. (2011). Association of the C(−1019)G 5-HT1A promoter polymorphism with exposure to stressors preceding hospitalization for bipolar depression. J. Affect. Disord. 132, 297–300. 10.1016/j.jad.2011.02.024, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

