Long-term vonoprazan therapy is effective for controlling symptomatic proton pump inhibitor-resistant gastroesophageal reflux disease
- PMID: 33585034
- PMCID: PMC7873583
- DOI: 10.3892/br.2021.1408
Long-term vonoprazan therapy is effective for controlling symptomatic proton pump inhibitor-resistant gastroesophageal reflux disease
Abstract
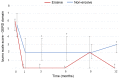
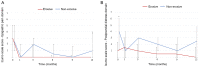
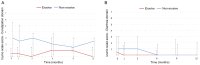
Vonoprazan, a novel potassium-competitive acid blocker, results in greater inhibition of gastric acid secretion than proton pump inhibitors (PPI). The aim of this study was to assess the long-term outcomes of patients with PPI-resistant gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) treated with vonoprazan. The medical records of patients with symptomatic GERD treated with vonoprazan for 1 year were retrospectively reviewed. Changes in abdominal symptoms were assessed using the Izumo scale, a self-reported questionnaire which is useful in evaluating the symptoms of GERD, epigastric pain, postprandial distress, constipation and diarrhea, and is commonly used in routine clinical practice. A total of 30 patients were included and stratified into a non-erosive (n=22) and erosive group (n=8). At baseline, postprandial distress symptoms were significantly greater in the non-erosive group compared with the erosive group (P=0.013). Even with vonoprazan therapy, symptoms of GERD in the non-erosive group were refractory compared with the erosive group, and required additional treatment in a larger proportion of patients (45 vs. 13%). GERD symptoms in the non-erosive group significantly improved from baseline and remained better after 1 year of vonoprazan therapy, similar to the erosive group. In addition, vonoprazan improved epigastric pain and postprandial distress symptoms in the non-erosive group, and 1 year of vonoprazan therapy did not aggravate constipation or diarrhea. In conclusion, 1 year of vonoprazan therapy improves GERD symptoms in patients with PPI-resistant GERD.
Keywords: GERD; PPI; dyspepsia; potassium-competitive acid blocker; therapeutic outcome.
Copyright © 2020, Spandidos Publications.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Vonoprazan 10 mg daily is effective for the treatment of patients with proton pump inhibitor-resistant gastroesophageal reflux disease.Biomed Rep. 2017 Sep;7(3):231-235. doi: 10.3892/br.2017.947. Epub 2017 Jul 20. Biomed Rep. 2017. PMID: 28894571 Free PMC article.
-
Long-term outcomes of patients with symptomatic gastroesophageal reflux disease treated with vonoprazan.Scand J Gastroenterol. 2018 Aug;53(8):897-904. doi: 10.1080/00365521.2018.1486883. Epub 2018 Jul 28. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2018. PMID: 30056768
-
Vonoprazan treatment improves gastrointestinal symptoms in patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease.Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2017 Dec;33(12):616-622. doi: 10.1016/j.kjms.2017.07.004. Epub 2017 Aug 5. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2017. PMID: 29132551 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
A systematic review and meta-analysis of the efficacy of vonoprazan for proton pump inhibitor-resistant gastroesophageal reflux disease.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024 May;39(5):796-805. doi: 10.1111/jgh.16475. Epub 2024 Jan 23. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024. PMID: 38263507
-
Vonoprazan causes symptomatic improvement in non-erosive gastroesophageal reflux disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. 2024 Jun;48(6):102373. doi: 10.1016/j.clinre.2024.102373. Epub 2024 May 7. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. 2024. PMID: 38719148
Cited by
-
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Obesity: Bariatric Surgery as Both the Cause and the Cure in the Morbidly Obese Population.J Clin Med. 2023 Aug 25;12(17):5543. doi: 10.3390/jcm12175543. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 37685616 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Incidence and type of adverse events in patients taking vonoprazan: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2023 Apr 20;16:17562848231167858. doi: 10.1177/17562848231167858. eCollection 2023. Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2023. PMID: 37113190 Free PMC article.
-
New Perspectives in Endoscopic Treatment of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Jun 14;13(12):2057. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13122057. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37370952 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Role of Potassium-competitive Acid Blockers in the Treatment of Gastric Acid-related Disorders].Korean J Helicobacter Up Gastrointest Res. 2023 Sep;23(3):167-173. doi: 10.7704/kjhugr.2023.0043. Epub 2023 Sep 8. Korean J Helicobacter Up Gastrointest Res. 2023. PMID: 40502664 Free PMC article. Review. Korean.
-
Progress on the Mechanism of Visceral Hypersensitivity in Nonerosive Reflux Disease.Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2022 Jan 20;2022:4785077. doi: 10.1155/2022/4785077. eCollection 2022. Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2022. PMID: 35096053 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Iwakiri K, Sano H, Tanaka Y, Kawami N, Umezawa M, Futagami S, Hoshihara Y, Nomura T, Miyashita M, Sakamoto C. Characteristics of symptomatic reflux episodes in patients with non-erosive reflux disease who have a positive symptom index on proton pump inhibitor therapy. Digestion. 2010;82:156–161. doi: 10.1159/000309483. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kagami T, Sahara S, Ichikawa H, Uotani T, Yamade M, Sugimoto M, Hamaya Y, Iwaizumi M, Osawa S, Sugimoto K, et al. Potent acid inhibition by vonoprazan in comparison with esomeprazole, with reference to CYP2C19 genotype. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2016;43:1048–1059. doi: 10.1111/apt.13588. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
