Expression and clinical significance of miR-1 and miR-133 in pre-diabetes
- PMID: 33585035
- PMCID: PMC7873585
- DOI: 10.3892/br.2021.1409
Expression and clinical significance of miR-1 and miR-133 in pre-diabetes
Abstract
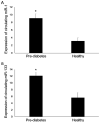
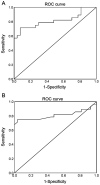
Pre-diabetes represents an intermediate state of altered glucose metabolism between normal glucose levels and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2D), and is considered a significant risk factor for the development of T2D and related complications. Early detection of pre-diabetes may allow for the use of timely and effective treatment strategies to prevent its progression. Circulating microRNAs (miRNAs/miRs) that reflect changes in diabetes-related tissues, including the pancreas, liver, skeletal and heart muscle, and adipose tissue are promising biomarkers of disease progression. In our previous study, it was demonstrated that the cardiac and skeletal muscle specific miR-1 and miR-133 are upregulated in the blood of patients with T2D and cardiovascular disease. Since both miRNAs have been shown to be implicated in insulin resistance, an important feature of pre-diabetes, we hypothesised that their expression may be increased prior to clinical diagnosis of T2D, and may thus serve as biomarkers for pre-diabetes. The expression levels of circulating miRNAs were evaluated by reverse transcription-quantitative PCR in whole blood samples from 55 subjects, including 28 pre-diabetes individuals with impaired fasting glucose (FG) and impaired glucose tolerance, and 27 healthy controls. The individuals with pre-diabetes exhibited significantly higher expression levels of miR-1 and miR-133 compared with the controls (P<0.05). Target prediction search revealed that both miR-1 and miR-133 target several pathways involved in the pathophysiology of diabetes. Pearson's correlation analysis revealed that the two miRNAs were positively correlated with blood glucose parameters, including FG, 2-h oral glucose tolerance test and glycated haemoglobin A1c levels, as well as with insulin resistance (P<0.05). Multivariate logistic regression analysis revealed that the two miRNAs were significantly and directly associated with pre-diabetes, and this association remained significant after adjustment for several confounding variables (P<0.05). Moreover, linear regression analysis showed that the Homeostatic Model Assessment-Insulin Resistance was the only significant predictor to be significantly associated with both miRNAs (P<0.05). In discriminating pre-diabetes individuals from healthy controls, the area under the curves (AUCs) of the receiver operating characteristic curves (ROCs) were 0.813 and 0.810 for miR-1 and miR-133 respectively (P<0.05). Despite the relatively small number of participants, the present study showed for the first time that circulating levels of miR-1 and miR-133 were increased in individuals with pre-diabetes, and they were associated with important features of pre-diabetes. Thus, they may serve as clinical biomarkers for the early-stages of T2D.
Keywords: biomarkers; circulating miRNAs; miR-1; miR-133; pre-diabetes.
Copyright © 2020, Spandidos Publications.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
