Exploring the Pattern Associated With Longitudinal Changes of β-Amyloid Deposition During Cognitively Normal Healthy Aging
- PMID: 33585514
- PMCID: PMC7874155
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2020.617173
Exploring the Pattern Associated With Longitudinal Changes of β-Amyloid Deposition During Cognitively Normal Healthy Aging
Abstract
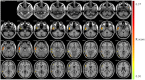
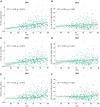
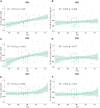
The aim of this study was to determine a pattern associated with longitudinal changes of β-amyloid (Aβ) deposition during cognitively normal(CN) healthy aging. We used 18F-florbetapir (AV-45) PET images of the brains of 207 cognitively normal subjects (CN1), obtained through the Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (ADNI), to identify the healthy aging pattern and 76 cognitively normal healthy subjects (CN2), obtained through the Xuanwu Hospital of Capital Medical University, Beijing, China, to verify it. A voxel-based correlation analysis of standardized uptake value ratio (SUVR) map image and age was conducted using the DPABI (Data Processing & Analysis of Brain Imaging) software to identify the pattern. The sum of squares due to errors (SSE), R-square (R2) and the root-mean-square error (RMSE) were calculated to assess the quality of curve fitting. Among them, R2 was proposed as the coherence coefficient, which was as an index to assess the correlation between SUVR value of the pattern and subjects' age. The pattern characterized by age-associated longitudinal changes of Aβ deposition was mainly distributed in the right middle and inferior temporal gyrus, the right temporal pole: middle temporal gyrus, the right inferior occipital gyrus, the right inferior frontal gyrus (triangular portion), and the right precentral gyrus. There were a significant positive correlation between the SUVR value of the pattern and age for each CN group (CN1: R2 = 0.120, p < 0.001 for quadratic model; CN2: R2 = 0.152, p = 0.002 for quadratic model). These findings suggest a pattern of changes in Aβ deposition that can be used to distinguish physiological changes from pathophysiological changes, constituting a new method for elucidating the neuropathological mechanism of Alzheimer's disease.
Keywords: 18F-AV-45 PET; brain; healthy aging; pattern; β-amyloid deposition.
Copyright © 2021 Xie, Yang, Liu, Zhang, Jiang, Han and the Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Quantitative 18F-AV1451 Brain Tau PET Imaging in Cognitively Normal Older Adults, Mild Cognitive Impairment, and Alzheimer's Disease Patients.Front Neurol. 2019 May 15;10:486. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2019.00486. eCollection 2019. Front Neurol. 2019. PMID: 31156534 Free PMC article.
-
A multicentre longitudinal study of flortaucipir (18F) in normal ageing, mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer's disease dementia.Brain. 2019 Jun 1;142(6):1723-1735. doi: 10.1093/brain/awz090. Brain. 2019. PMID: 31009046 Free PMC article.
-
Relationships between flortaucipir PET tau binding and amyloid burden, clinical diagnosis, age and cognition.Brain. 2017 Mar 1;140(3):748-763. doi: 10.1093/brain/aww334. Brain. 2017. PMID: 28077397 Free PMC article.
-
Longitudinal Assessment of Amyloid-β Deposition by [18F]-Flutemetamol PET Imaging Compared With [11C]-PIB Across the Spectrum of Alzheimer's Disease.Front Aging Neurosci. 2019 Sep 11;11:251. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2019.00251. eCollection 2019. Front Aging Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31572167 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of β-amyloid positivity on cerebral metabolism in cognitively normal seniors.Alzheimers Dement. 2016 Dec;12(12):1250-1258. doi: 10.1016/j.jalz.2016.06.003. Epub 2016 Aug 27. Alzheimers Dement. 2016. PMID: 27445158
Cited by
-
Protein fibril aggregation on red blood cells: a potential biomarker to distinguish neurodegenerative diseases from healthy aging.Brain Commun. 2024 Jun 13;6(3):fcae180. doi: 10.1093/braincomms/fcae180. eCollection 2024. Brain Commun. 2024. PMID: 38873003 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of NF-kB and MAPK mediated Proinflammatory microenvironment on renal aging and amyloid deposition in elder rats.Sci Rep. 2025 Aug 18;15(1):30188. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-14559-y. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40825962 Free PMC article.
-
Protein Coaggregation in Caribbean Atypical Parkinsonism: The Contribution of Annonacin.Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 2025 Aug;51(4):e70026. doi: 10.1111/nan.70026. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 2025. PMID: 40702589 Free PMC article.
-
Voxel-based evaluation for [18F] Florbetaben brain β-amyloid positron emission tomography of healthy control, mild cognitive impairment, and Alzheimer's disease.Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2024 Dec 5;14(12):9146-9156. doi: 10.21037/qims-24-1100. Epub 2024 Nov 29. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2024. PMID: 39698592 Free PMC article.
-
Tracer-specific reference tissues selection improves detection of 18 F-FDG, 18 F-florbetapir, and 18 F-flortaucipir PET SUVR changes in Alzheimer's disease.Hum Brain Mapp. 2022 May;43(7):2121-2133. doi: 10.1002/hbm.25774. Epub 2022 Feb 15. Hum Brain Mapp. 2022. PMID: 35165964 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

