A Prospective Controlled Trial to Evaluate Safety and Efficacy of in vitro Expanded Recipient Regulatory T Cell Therapy and Tocilizumab Together With Donor Bone Marrow Infusion in HLA-Mismatched Living Donor Kidney Transplant Recipients (Trex001)
- PMID: 33585521
- PMCID: PMC7873436
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2020.634260
A Prospective Controlled Trial to Evaluate Safety and Efficacy of in vitro Expanded Recipient Regulatory T Cell Therapy and Tocilizumab Together With Donor Bone Marrow Infusion in HLA-Mismatched Living Donor Kidney Transplant Recipients (Trex001)
Abstract
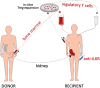
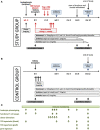
Background: The induction of donor-specific immunological tolerance could improve outcome after kidney transplantation. However, no tolerance protocol is available for routine clinical use. Chimerism-based regimens hold promise, but their widespread application is impeded in part by unresolved safety issues. This study tests the hypothesis that therapy with polyclonal recipient regulatory T cells (Tregs) and anti-IL6R (tocilizumab) leads to transient chimerism and achieves pro-tolerogenic immunomodulation in kidney transplant recipients also receiving donor bone marrow (BM) without myelosuppressive conditioning of the recipient. Methods/design: A prospective, open-label, controlled, single-center, phase I/IIa academic study is performed in HLA-mismatched living donor kidney transplant recipients. Study group: Recipients of the study group receive in vitro expanded recipient Tregs and a donor bone marrow cell infusion within 3 days after transplantation and tocilizumab for the first 3 weeks post-transplant. In addition they are treated with thymoglobulin, belatacept, sirolimus, and steroids as immunosuppression. Starting 6 months post-transplant, sirolimus and steroids are withdrawn in a step-wise manner in stable patients. Control group: Recipients of the control group are treated with thymoglobulin, belatacept, sirolimus, and steroids as immunosuppression. Co-primary endpoints of safety (impaired graft function [eGFR <35 mL/min/1.73 m2], graft-vs.-host disease or patient death by 12 months) and efficacy (total leukocyte donor chimerism within 28 days post-transplant) are assessed. Secondary endpoints include frequency of biopsy-proven acute rejection episodes and subclinical rejection episodes on surveillance biopsies, assessment of kidney graft function, and the evaluation whether the study protocol leads to detectable changes in the immune system indicative of pro-tolerogenic immune modulation. Discussion: The results of this trial will provide evidence whether treatment with recipient Tregs and donor BM is feasible, safe and efficacious in leading to transient chimerism. If successful, this combination cell therapy has the potential to become a novel treatment option for immunomodulation in organ transplantation without the toxicities associated with myelosuppressive recipient conditioning. Trial registration: European Clinical Trials Database EudraCT Nr 2018-003142-16 and clinicaltrials.gov NCT03867617.
Keywords: belatacept; bone marrow; cell therapy; chimerism; kidney transplantation; regulatory T cells; tocilizumab; tolerance.
Copyright © 2021 Oberbauer, Edinger, Berlakovich, Kalhs, Worel, Heinze, Wolzt, Lion and Wekerle.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Billingham RE, Lampkin GH, Medawar PB, Williams HL. Tolerance to homografts, twin diagnosis, and the freemartin condition in cattle. Heredity. (1952) 6:200–12. 10.1038/hdy.1952.20 - DOI
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

