The Interplay Between Diet and the Epigenome in the Pathogenesis of Type-1 Diabetes
- PMID: 33585535
- PMCID: PMC7876257
- DOI: 10.3389/fnut.2020.612115
The Interplay Between Diet and the Epigenome in the Pathogenesis of Type-1 Diabetes
Abstract
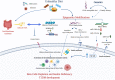
The autoimmune disease, Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus (T1DM), results in the destruction of pancreatic β-cells, and the International Diabetes Federation reports that its incidence is increasing worldwide. T1DM is a complex disease due to the interaction between genetic and environmental factors. Certain dietary patterns and nutrients are known to cause epigenetic modifications in physiological conditions and diseases. However, the interplay between diet and epigenetics is not yet well-understood in the context of T1DM. Several studies have described epigenetic mechanisms involved in the autoimmune reactions that destroy the β-cells, but few explored diet components as potential triggers for epigenetic modifications. Clarifying the link between diet and epigenome can provide new insights into the pathogenesis of T1DM, potentially leading to new diagnostic and therapeutic approaches. In this mini review, we shed light on the influence of the diet-epigenome axis on the pathophysiology of T1DM.
Keywords: DNA methylation; diet; epigenetics; histone modifications; micro-RNA; type 1 diabetes.
Copyright © 2021 Kohil, Al-Asmakh, Al-Shafai and Terranegra.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

