Intravenous and Oral Fluid Therapy in Neonatal Calves With Diarrhea or Sepsis and in Adult Cattle
- PMID: 33585594
- PMCID: PMC7873366
- DOI: 10.3389/fvets.2020.603358
Intravenous and Oral Fluid Therapy in Neonatal Calves With Diarrhea or Sepsis and in Adult Cattle
Abstract
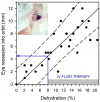
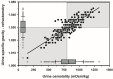
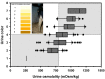
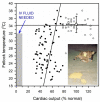
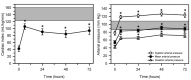
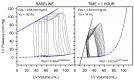
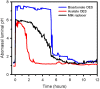
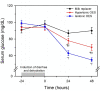
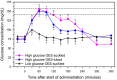
Optimal fluid therapy protocols in neonatal calves and adult cattle are based on consideration of signalment, history, and physical examination findings, and individually tailored whenever laboratory analysis is available. Measurement of the magnitude of eye recession, duration of skin tenting in the lateral neck region, and urine specific gravity by refractometry provide the best estimates of hydration status in calves and cattle. Intravenous and oral electrolyte solutions (OES) are frequently administered to critically ill calves and adult cattle. Application of physicochemical principles indicates that 0.9% NaCl, Ringer's solution, and 5% dextrose are equally acidifying, lactated Ringer's and acetated Ringer's solution are neutral to mildly acidifying, and 1.3-1.4% sodium bicarbonate solutions are strongly alkalinizing in cattle. Four different crystalloid solutions are recommended for intravenous fluid therapy in dehydrated or septic calves and dehydrated adult cattle: (1) lactated Ringer's solution and acetated Ringer's solution for dehydrated calves, although neither solution is optimized for administration to neonatal calves or adult cattle; (2) isotonic (1.3%) or hypertonic (5.0 or 8.4%) solutions of sodium bicarbonate for the treatment of calves with diarrhea and severe strong ion (metabolic) acidosis and hyponatremia, and adult cattle with acute ruminal acidosis; (3) Ringer's solution for the treatment of metabolic alkalosis in dehydrated adult cattle, particularly lactating dairy cattle; and (4) hypertonic NaCl solutions (7.2%) and an oral electrolyte solution or water load for the rapid resuscitation of dehydrated neonatal calves and adult cattle. Much progress has been made since the 1970's in identifying important attributes of an OES for diarrheic calves. Important components of an OES for neonatal calves are osmolality, sodium concentration, the effective SID that reflects the concentration of alkalinizing agents, and the energy content. The last three factors are intimately tied to the OES osmolality and the abomasal emptying rate, and therefore the rate of sodium delivery to the small intestine and ultimately the rate of resuscitation. An important need in fluid and electrolyte therapy for adult ruminants is formulation of a practical, effective, and inexpensive OES.
Keywords: acidosis; acid–base balance; alkalosis; fluid therapy; oral electrolyte solution; osmolality.
Copyright © 2021 Constable, Trefz, Sen, Berchtold, Nouri, Smith and Grünberg.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Dillane P, Krump L, Kennedy E, Sayers RG, Sayers GP. Determining the predictive capability of a Clinical Assessment Scoring Chart to differentiate severity of the clinical consequences of neonatal calf diarrhea relative to gold-standard blood gas analysis. PLoS ONE. (2020) 15:e0230708. 10.1371/journal.pone.0230708 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Constable PD, Walker PG, Morin DE, Foreman JH. Clinical and laboratory assessment of hydration status of neonatal calves with diarrhea. J Am Vet Med Assoc. (1998) 212:991–6. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

