Tandem MS-Based Metabolite Profiling of 19,20-Epoxycytochalasin C Reveals the Importance of a Hydroxy Group at the C7 Position for Biological Activity
- PMID: 33585752
- PMCID: PMC7876698
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.0c05307
Tandem MS-Based Metabolite Profiling of 19,20-Epoxycytochalasin C Reveals the Importance of a Hydroxy Group at the C7 Position for Biological Activity
Abstract
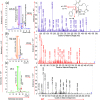
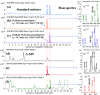
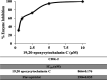
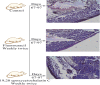
Seven cytochalasins, 19,20-epoxycytochalasin N, cytochalasin P1, deacetyl 19,20-epoxycytochalasin C, 19,20-epoxycytochalasin D, 19,20-epoxycytochalasin C, cytochalasin D, and cytochalasin C, were isolated from a fungal (Rosellinia sanctae-cruciana) crude extract. A cytotoxicity assay (sulforhodamine B) was performed on a series of cancer cell lines: HT-29, A-549, PC-3, HCT-116, SW-620, and MCF-7. Simultaneously, the liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS)/MS profile of 19,20-epoxycytochalasin C-treated cell lines revealed that 19,20-epoxycytochalasin C (m/z 524.25) oxidized to a metabolite of m/z 522.25 Da (-2 Da (-2H) from 19,20-epoxycytochalasin C). Further chemical oxidation of 19,20-epoxycytochalasin C using the Dess-Martin reagent produced an identical metabolite. It has been noticed that the parent molecule (19,20-epoxycytochalasin C) showed an IC50 of 650 nM (on HT-29), whereas for the oxidized metabolite (m/z 522.24) of 19,20-epoxycytochalasin C, the IC50 was >10 μM. It is clear that the parent molecule had 16 times higher cytotoxic potential as compared to the oxidized metabolite. The spectroscopic investigation indicated that the oxidation of the hydroxyl (-OH) group occurred at the C7 position in 19,20-epoxycyctochalsin C and led to the inactivation of 19,20-epoxycytochalasin C. Further, cell cycle analysis and histopathological evidence support the findings, and CDK2 could be a possible target of 19,20-epoxycyctochalasin C.
© 2021 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
LC-PDA-MS/MS-Based Dereplication Guided Isolation of a New Optical Isomer of 19,20-Epoxycytochalasin-N and Its Cytotoxic Activity.ACS Omega. 2022 Aug 10;7(33):29135-29141. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.2c03037. eCollection 2022 Aug 23. ACS Omega. 2022. PMID: 36033687 Free PMC article.
-
New cytochalasin from Rosellinia sanctae-cruciana, an endophytic fungus of Albizia lebbeck.J Appl Microbiol. 2018 Jul;125(1):111-120. doi: 10.1111/jam.13764. Epub 2018 May 20. J Appl Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29573314
-
Six 19,20-epoxycytochalasans from endophytic Diaporthe sp. RJ-47.Nat Prod Res. 2022 Jul;36(13):3375-3380. doi: 10.1080/14786419.2020.1859504. Epub 2020 Dec 16. Nat Prod Res. 2022. PMID: 33325741
-
Rapid screening and identification of cytochalasins by electrospray tandem mass spectrometry.J Mass Spectrom. 2002 Mar;37(3):283-91. doi: 10.1002/jms.282. J Mass Spectrom. 2002. PMID: 11921369
-
Vitamin D metabolite profiling using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS).J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2016 Nov;164:110-114. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2015.09.026. Epub 2015 Sep 26. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2016. PMID: 26409684 Review.
Cited by
-
Biodiversity and Bioactive Potential of Actinomycetes from Unexplored High Altitude Regions of Kargil, India.Indian J Microbiol. 2024 Mar;64(1):110-124. doi: 10.1007/s12088-023-01133-1. Epub 2023 Dec 11. Indian J Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38468743 Free PMC article.
-
LC-PDA-MS/MS-Based Dereplication Guided Isolation of a New Optical Isomer of 19,20-Epoxycytochalasin-N and Its Cytotoxic Activity.ACS Omega. 2022 Aug 10;7(33):29135-29141. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.2c03037. eCollection 2022 Aug 23. ACS Omega. 2022. PMID: 36033687 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Luo Y.-F.; Zhang M.; Dai J.-G.; Pedpradab P.; Wang W.-J.; Wu J. Cytochalasins from mangrove endophytic fungi Phomopsis spp. xy21 and xy22. Phytochem. Lett. 2016, 17, 162–166. 10.1016/j.phytol.2016.07.027. - DOI
-
- Aldridge D. C.; Armstrong J. J.; Speake R. N.; Turner W. B. The cytochalasins, a new class of biologically active mould metabolites. Chem. Commun. 1967, 26–27. 10.1039/c19670000026. - DOI
-
- Zhang X.-Q.; Guan F.-F.; Li D.-B.; Wang C.-Y.; Shao C.-L. Preparation, Structure Elucidation, and Antiviral and Cytotoxic Activities of Acylation Derivatives of Cytochalasin B. Chem. Nat. Compd. 2017, 53, 109–113. 10.1007/s10600-017-1921-7. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

