Metabolomic Analysis of Skin Biopsies from Patients with Atopic Dermatitis Reveals Hallmarks of Inflammation, Disrupted Barrier Function and Oxidative Stress
- PMID: 33585945
- PMCID: PMC9366688
- DOI: 10.2340/00015555-3766
Metabolomic Analysis of Skin Biopsies from Patients with Atopic Dermatitis Reveals Hallmarks of Inflammation, Disrupted Barrier Function and Oxidative Stress
Abstract
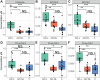
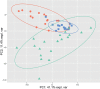
The main objectives of this study were to characterize the metabolomic profile of lesional skin of patients with atopic dermatitis, and to compare it with non- lesional skin of patients with atopic dermatitis and skin of controls with no dermatological disease. Skin-punch biopsies were collected from 15 patients and 17 controls. Targeted analysis of 188 metabolites was conducted. A total of 77 metabolites and their ratios were found, which differed significantly between lesional skin of atopic dermatitis, non-lesional skin of atopic dermatitis and skin of controls. The metabolites were members of the following classes: amino acids, biogenic amines, acylcarnitines, sphingomyelins or phosphatidylcholines, and the most significant differences be-tween the groups compared were in the concentrations of putrescine, SM.C26.0 and SM.C26.1. The alterations in metabolite levels indicate inflammation, impaired barrier function, and susceptibility to oxidative stress in atopic skin.
Keywords: biomarkers; dermatology; metabolomics; atopic dermatitis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Metabolomic Differences between the Skin and Blood Sera of Atopic Dermatitis and Psoriasis.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Oct 27;23(21):13001. doi: 10.3390/ijms232113001. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36361789 Free PMC article.
-
Use of Tape Strips to Detect Immune and Barrier Abnormalities in the Skin of Children With Early-Onset Atopic Dermatitis.JAMA Dermatol. 2019 Dec 1;155(12):1358-1370. doi: 10.1001/jamadermatol.2019.2983. JAMA Dermatol. 2019. PMID: 31596431 Free PMC article.
-
Reevaluation of the non-lesional dry skin in atopic dermatitis by acute barrier disruption: an abnormal permeability barrier homeostasis with defective processing to generate ceramide.Arch Dermatol Res. 2014 Jul;306(5):427-40. doi: 10.1007/s00403-013-1430-x. Epub 2013 Nov 23. Arch Dermatol Res. 2014. PMID: 24271939
-
Cutting Edge of the Pathogenesis of Atopic Dermatitis: Sphingomyelin Deacylase, the Enzyme Involved in Its Ceramide Deficiency, Plays a Pivotal Role.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Feb 5;22(4):1613. doi: 10.3390/ijms22041613. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33562655 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Skin barrier function, epidermal proliferation and differentiation in eczema.J Dermatol Sci. 2006 Sep;43(3):159-69. doi: 10.1016/j.jdermsci.2006.06.003. Epub 2006 Aug 2. J Dermatol Sci. 2006. PMID: 16887338 Review.
Cited by
-
Metabolomic Differences between the Skin and Blood Sera of Atopic Dermatitis and Psoriasis.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Oct 27;23(21):13001. doi: 10.3390/ijms232113001. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36361789 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-omics analyses reveal interactions between the skin microbiota and skin metabolites in atopic dermatitis.Front Microbiol. 2024 Mar 15;15:1349674. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1349674. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38559353 Free PMC article.
-
Changes in Lipoprotein Particles in the Blood Serum of Patients with Lichen Planus.Metabolites. 2023 Jan 6;13(1):91. doi: 10.3390/metabo13010091. Metabolites. 2023. PMID: 36677016 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the Metabolic Effects of a Herbal Remedy of Asarum sieboldii, Platycodon grandiflorum, and Cinnamomum cassia Extracts: Unraveling Its Therapeutic Potential as a Topical Application for Atopic Dermatitis Treatment.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 May 2;13(5):563. doi: 10.3390/antiox13050563. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38790668 Free PMC article.
-
Atopic Dermatitis and Psoriasis: Similarities and Differences in Metabolism and Microbiome.Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2024 Jun;66(3):294-315. doi: 10.1007/s12016-024-08995-3. Epub 2024 Jul 2. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38954264 Review.
References
-
- Yang EJ, Beck KM, Sekhon S, Bhutani T, Koo J. The impact of pediatric atopic dermatitis on families: a review. Pediatr Dermatol 2019; 36: 66–71. - PubMed
-
- Thyssen JP, Hamann CR, Skov L, Egeberg A, Linneberg A, Dantoft TM, et al. . Atopic dermatitis is associated with anxiety, depression, and suicidal ideation, but not with psychiatric hospitalization or suicide. Allergy 2018; 73: 214–220. - PubMed
-
- Nutten S. Atopic dermatitis: global epidemiology and risk factors. Ann Nutr Metab 2015; 66: 8–16. - PubMed
-
- Asher MI, Montefort S, Bjorksten B, Lai CKW, Strachan DP, Weiland SK, et al. . Worldwide time trends in the prevalence of symptoms of asthma, allergic rhinoconjunctivitis, and eczema in childhood: ISAAC Phases One and Three repeat multicountry cross-sectional surveys. Lancet 2006; 368: 733–743. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

