Low free thyroxine and normal thyroid-stimulating hormone in infants and children: possible causes and diagnostic work-up
- PMID: 33585976
- PMCID: PMC8195777
- DOI: 10.1007/s00431-021-03976-6
Low free thyroxine and normal thyroid-stimulating hormone in infants and children: possible causes and diagnostic work-up
Abstract
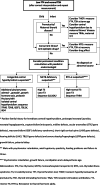
Screening for hypo- or hyperthyroidism in adults is generally done by measuring the serum thyrotropin (thyroid-stimulating hormone, TSH) concentration. This is an efficient approach in case of suspected acquired thyroid disease. However, in infants and children, congenital hypothalamus-pituitary-thyroid (HPT) axis disorders also need to be considered, including primary and central congenital hypothyroidism, and even rarer thyroid hormone receptor and transporter defects. In primary congenital hypothyroidism, TSH will be elevated, but in the other congenital HPT axis disorders, TSH is usually within the normal range. Free thyroxine (FT4) assessment is essential for the diagnosis in these conditions.Conclusion: Here we discuss a number of rare congenital HPT axis disorders in which TSH is normal, but FT4 is low, and provide a clinical algorithm to distinguish between these disorders. What is Known: • A single thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) measurement is an appropriate screening method for primary hypothyroidism. • For central hypothyroidism and rare thyroid hormone receptor and transporter defects a free thyroxine (FT4) measurement is essential for the diagnosis because TSH is usually normal. What is New: • Here we present a new problem-oriented clinical algorithm including a diagnostic flow-chart for low FT4 and normal TSH in infants and children.
Keywords: Central hypothyroidism; Children; FT4; TSH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Eerdekens A, Langouche L, Van den Berghe G, Verhaeghe J, Naulaers G, Vanhole C. Review shows that thyroid hormone substitution could benefit transient hypothyroxinaemia of prematurity but treatment strategies need to be clarified. Acta Paediatr. 2019;108(5):792–805. doi: 10.1111/apa.14685. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical