Recent trends in smartphone-based detection for biomedical applications: a review
- PMID: 33586007
- PMCID: PMC7882471
- DOI: 10.1007/s00216-021-03184-z
Recent trends in smartphone-based detection for biomedical applications: a review
Abstract
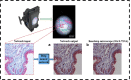
Smartphone-based imaging devices (SIDs) have shown to be versatile and have a wide range of biomedical applications. With the increasing demand for high-quality medical services, technological interventions such as portable devices that can be used in remote and resource-less conditions and have an impact on quantity and quality of care. Additionally, smartphone-based devices have shown their application in the field of teleimaging, food technology, education, etc. Depending on the application and imaging capability required, the optical arrangement of the SID varies which enables them to be used in multiple setups like bright-field, fluorescence, dark-field, and multiple arrays with certain changes in their optics and illumination. This comprehensive review discusses the numerous applications and development of SIDs towards histopathological examination, detection of bacteria and viruses, food technology, and routine diagnosis. Smartphone-based devices are complemented with deep learning methods to further increase the efficiency of the devices. Graphical Abstract.
Keywords: Deep learning; Diagnostics; Fluorescence imaging; Immunoassay; Optical microscopy; Smartphone.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- McCracken KE, Yoon JY. Recent approaches for optical smartphone sensing in resource-limited settings: a brief review. Anal Methods. 2016;8(36):6591–6601. doi: 10.1039/C6AY01575A. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

