Psychosocial interventions for adults with newly diagnosed chronic disease: A systematic review
- PMID: 33586486
- PMCID: PMC9092922
- DOI: 10.1177/1359105321995916
Psychosocial interventions for adults with newly diagnosed chronic disease: A systematic review
Abstract
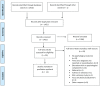
While the need for psychosocial interventions in the early formative period of chronic disease diagnosis is widely acknowledged, little is known about the currently available interventions and what they entail. This review sought to collate existing interventions to synthesize their active ingredients. A systematic search on five electronic databases yielded 2910 records, 12 of which were eligible for this review. Evidence synthesis revealed three broad categories of interventions which used at least two out of eight active techniques. Future studies should adhere to known frameworks for intervention development, and focus on developing core outcome measures to enhance evidence synthesis.
Keywords: adaptation; chronic disease; coping; newly diagnosed; psychosocial intervention; social support.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Ahrens S, Elsner H. (1981) Empirische Untersuchungen zum Krankheitskonzept neurotischer, psychosomatischer und somatisch kranker Patienten (Teil II). Medizinische Psychologie 7: 95–109.
-
- Andresen EM, Malmgren JA, Carter WB, et al. (1994) Screening for depression in well older adults: Evaluation of a short form of the CES-D. American Journal of Preventive Medicine 10(2): 77–84. - PubMed
-
- Aromataris E, Riitano D. (2014) Systematic reviews: Constructing a search strategy and searching for evidence. American Journal of Nursing 114(5): 49–56. - PubMed
-
- Bauman LJ, Weiss E. (1995) Multidimensional Social Support Inventory: Revised. New York: Albert Einstein College of Medicine.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources