Pancreatic β-cell heterogeneity in health and diabetes: classes, sources, and subtypes
- PMID: 33586491
- PMCID: PMC8238131
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpendo.00649.2020
Pancreatic β-cell heterogeneity in health and diabetes: classes, sources, and subtypes
Abstract
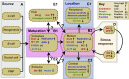
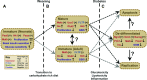
Pancreatic β-cells perform glucose-stimulated insulin secretion, a process at the center of type 2 diabetes etiology. Efforts to understand how β-cells behave in healthy and stressful conditions have revealed a wide degree of morphological, functional, and transcriptional heterogeneity. Sources of heterogeneity include β-cell topography, developmental origin, maturation state, and stress response. Advances in sequencing and imaging technologies have led to the identification of β-cell subtypes, which play distinct roles in the islet niche. This review examines β-cell heterogeneity from morphological, functional, and transcriptional perspectives, and considers the relevance of topography, maturation, development, and stress response. It also discusses how these factors have been used to identify β-cell subtypes, and how heterogeneity is impacted by diabetes. We examine open questions in the field and discuss recent technological innovations that could advance understanding of β-cell heterogeneity in health and disease.
Keywords: diabetes; insulin secretion; β-cell heterogeneity; β-cell subtype.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P30 DK056341/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 DK108742/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30DK020579/HHS | NIH | National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK)
- F31 DK125023-01/HHS | NIH | National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK)
- F31 DK125023/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

