The lung microenvironment shapes a dysfunctional response of alveolar macrophages in aging
- PMID: 33586677
- PMCID: PMC7919859
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI140299
The lung microenvironment shapes a dysfunctional response of alveolar macrophages in aging
Abstract
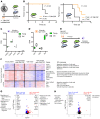
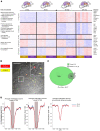
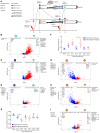
Alveolar macrophages orchestrate the response to viral infections. Age-related changes in these cells may underlie the differential severity of pneumonia in older patients. We performed an integrated analysis of single-cell RNA-Seq data that revealed homogenous age-related changes in the alveolar macrophage transcriptome in humans and mice. Using genetic lineage tracing with sequential injury, heterochronic adoptive transfer, and parabiosis, we found that the lung microenvironment drove an age-related resistance of alveolar macrophages to proliferation that persisted during influenza A viral infection. Ligand-receptor pair analysis localized these changes to the extracellular matrix, where hyaluronan was increased in aged animals and altered the proliferative response of bone marrow-derived macrophages to granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF). Our findings suggest that strategies targeting the aging lung microenvironment will be necessary to restore alveolar macrophage function in aging.
Keywords: Aging; Immunology; Influenza; Innate immunity; Macrophages.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures






References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- I01 CX001777/CX/CSRD VA/United States
- R01 AR073270/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AG026647/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD011996/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- K08 HL128867/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG049665/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI135964/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL153312/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA060553/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 ES015024/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- K99 AG068544/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL145478/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 ES027792/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL149883/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL134800/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL076139/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AR074902/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 AG057296/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL071643/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K08 HL146943/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 ES026718/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL147290/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL154686/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL147575/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL134375/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R56 HL135124/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG054407/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

