GWAS of three molecular traits highlights core genes and pathways alongside a highly polygenic background
- PMID: 33587031
- PMCID: PMC7884075
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.58615
GWAS of three molecular traits highlights core genes and pathways alongside a highly polygenic background
Abstract
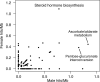
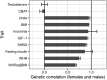
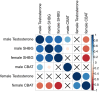
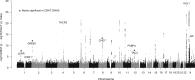
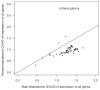
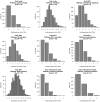
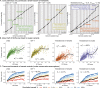
Genome-wide association studies (GWAS) have been used to study the genetic basis of a wide variety of complex diseases and other traits. We describe UK Biobank GWAS results for three molecular traits-urate, IGF-1, and testosterone-with better-understood biology than most other complex traits. We find that many of the most significant hits are readily interpretable. We observe huge enrichment of associations near genes involved in the relevant biosynthesis, transport, or signaling pathways. We show how GWAS data illuminate the biology of each trait, including differences in testosterone regulation between females and males. At the same time, even these molecular traits are highly polygenic, with many thousands of variants spread across the genome contributing to trait variance. In summary, for these three molecular traits we identify strong enrichment of signal in putative core gene sets, even while most of the SNP-based heritability is driven by a massively polygenic background.
Keywords: biomarkers; complex traits; genetics; genome-wide association study; genomics; human; igf-1; testosterone; urate.
© 2021, Sinnott-Armstrong et al.
Conflict of interest statement
NS, SN, MR, JP No competing interests declared
Figures
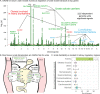

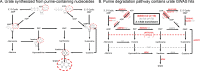
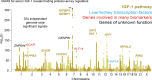
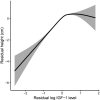
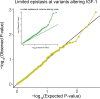
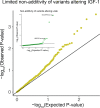
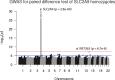
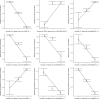
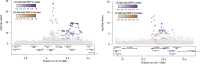


Similar articles
-
Haplotype function score improves biological interpretation and cross-ancestry polygenic prediction of human complex traits.Elife. 2024 Apr 19;12:RP92574. doi: 10.7554/eLife.92574. Elife. 2024. PMID: 38639992 Free PMC article.
-
Variable prediction accuracy of polygenic scores within an ancestry group.Elife. 2020 Jan 30;9:e48376. doi: 10.7554/eLife.48376. Elife. 2020. PMID: 31999256 Free PMC article.
-
Estimation of non-null SNP effect size distributions enables the detection of enriched genes underlying complex traits.PLoS Genet. 2020 Jun 15;16(6):e1008855. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1008855. eCollection 2020 Jun. PLoS Genet. 2020. PMID: 32542026 Free PMC article.
-
The omnigenic model and polygenic prediction of complex traits.Am J Hum Genet. 2021 Sep 2;108(9):1558-1563. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2021.07.003. Epub 2021 Jul 30. Am J Hum Genet. 2021. PMID: 34331855 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Leveraging GWAS for complex traits to detect signatures of natural selection in humans.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2018 Dec;53:9-14. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2018.05.012. Epub 2018 Jun 16. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2018. PMID: 29913353 Review.
Cited by
-
The pathogenesis of gout: molecular insights from genetic, epigenomic and transcriptomic studies.Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2024 Aug;20(8):510-523. doi: 10.1038/s41584-024-01137-1. Epub 2024 Jul 11. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2024. PMID: 38992217 Review.
-
Sex-Hormone-Binding Globulin Gene Polymorphisms and Breast Cancer Risk in Caucasian Women of Russia.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Feb 11;25(4):2182. doi: 10.3390/ijms25042182. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38396861 Free PMC article.
-
Polygenic risk score phenome-wide association study reveals an association between endometriosis and testosterone.BMC Med. 2023 Dec 5;21(1):482. doi: 10.1186/s12916-023-03184-z. BMC Med. 2023. PMID: 38049874 Free PMC article.
-
Strain-Specific Liver Metabolite Profiles in Medaka.Metabolites. 2021 Oct 29;11(11):744. doi: 10.3390/metabo11110744. Metabolites. 2021. PMID: 34822402 Free PMC article.
-
Multivariate genetic architecture reveals testosterone-driven sexual antagonism in contemporary humans.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 Jun 11;121(24):e2404364121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2404364121. Epub 2024 Jun 4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024. PMID: 38833469 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

