SNPC-1.3 is a sex-specific transcription factor that drives male piRNA expression in C. elegans
- PMID: 33587037
- PMCID: PMC7884074
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.60681
SNPC-1.3 is a sex-specific transcription factor that drives male piRNA expression in C. elegans
Abstract
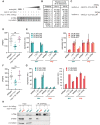
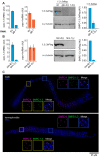
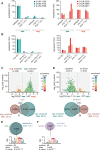
Piwi-interacting RNAs (piRNAs) play essential roles in silencing repetitive elements to promote fertility in metazoans. Studies in worms, flies, and mammals reveal that piRNAs are expressed in a sex-specific manner. However, the mechanisms underlying this sex-specific regulation are unknown. Here we identify SNPC-1.3, a male germline-enriched variant of a conserved subunit of the small nuclear RNA-activating protein complex, as a male-specific piRNA transcription factor in Caenorhabditis elegans. SNPC-1.3 colocalizes with the core piRNA transcription factor, SNPC-4, in nuclear foci of the male germline. Binding of SNPC-1.3 at male piRNA loci drives spermatogenic piRNA transcription and requires SNPC-4. Loss of snpc-1.3 leads to depletion of male piRNAs and defects in male-dependent fertility. Furthermore, TRA-1, a master regulator of sex determination, binds to the snpc-1.3 promoter and represses its expression during oogenesis. Loss of TRA-1 targeting causes ectopic expression of snpc-1.3 and male piRNAs during oogenesis. Thus, sexually dimorphic regulation of snpc-1.3 expression coordinates male and female piRNA expression during germline development.
Keywords: C. elegans; TRA-1; chromosomes; gene expression; genetics; genomics; germline development; piRNA; sex determination; spermatogenesis; transcription.
© 2021, Choi et al.
Conflict of interest statement
CC, RT, MS, SF, JM, BM, EX, MH, MS, TM, JY, SJ, JK No competing interests declared
Figures


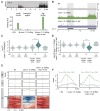



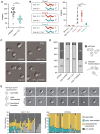
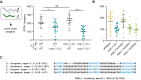


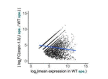
References
-
- Aravin A, Gaidatzis D, Pfeffer S, Lagos-Quintana M, Landgraf P, Iovino N, Morris P, Brownstein MJ, Kuramochi-Miyagawa S, Nakano T, Chien M, Russo JJ, Ju J, Sheridan R, Sander C, Zavolan M, Tuschl T. A novel class of small RNAs bind to MILI protein in mouse testes. Nature. 2006;442:203–207. doi: 10.1038/nature04916. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

