Aggregated Tau Measured by Visual Interpretation of Flortaucipir Positron Emission Tomography and the Associated Risk of Clinical Progression of Mild Cognitive Impairment and Alzheimer Disease: Results From 2 Phase III Clinical Trials
- PMID: 33587110
- PMCID: PMC7885097
- DOI: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2020.5505
Aggregated Tau Measured by Visual Interpretation of Flortaucipir Positron Emission Tomography and the Associated Risk of Clinical Progression of Mild Cognitive Impairment and Alzheimer Disease: Results From 2 Phase III Clinical Trials
Abstract
Importance: Flortaucipir positron emission tomography (PET) scans, rated with a novel, US Food and Drug Administration-approved, clinically applicable visual interpretation method, provide valuable information regarding near-term clinical progression of patients with Alzheimer disease (AD) or mild cognitive impairment (MCI).
Objective: To evaluate the association between flortaucipir PET visual interpretation and patients' near-term clinical progression.
Design/setting/participants: Two prospective, open-label, longitudinal studies were conducted from December 2014 to September 2019. Study 1 screened 298 patients and enrolled 160 participants who had a flortaucipir scan at baseline visit. Study 2 selected 205 participants from the AMARANTH trial, which was terminated after futility analysis. Out of the 2218 AMARANTH participants, 424 had a flortaucipir scan around randomization, but 219 did not complete 18-month clinical dementia rating (CDR) assessments and thus were excluded. In both studies, all participants were diagnosed as clinically impaired, and they were longitudinally followed up for approximately 18 months after baseline.
Main outcomes and measures: Flortaucipir scans were rated as either advanced or nonadvanced AD pattern using a predetermined visual interpretation method. The CDR sum of box (CDR-SB) score was used as primary clinical end point measurement in both studies.
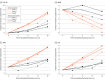
Results: Of the 364 study participants who had readable scans, 48% were female (n = 174 of 364), and the mean (SD) age was 71.8 (8.7) years. Two hundred forty participants were rated as having an advanced AD pattern. At 18 months follow-up, 70% of those with an advanced AD pattern (n = 147 of 210) had 1 point or more increase in CDR-SB, an event predefined as clinically meaningful deterioration. In contrast, only 46% of those with a nonadvanced AD pattern scan (n = 48 of 105) experienced the same event (risk ratio [RR], 1.40; 95% CI, 1.11-1.76; P = .005). The adjusted mean CDR-SB changes were 2.28 and 0.98 for advanced and nonadvanced AD pattern groups, respectively (P < .001). Analyses with other clinical end point assessments, as well as analyses with each individual study's data, consistently indicated a higher risk of clinical deterioration associated with an advanced AD scan pattern.
Conclusions and relevance: These results suggest that flortaucipir PET scans, when interpreted with an US Food and Drug Administration-approved, clinically applicable visual interpretation method, may provide valuable information regarding the risk of clinical deterioration over 18 months among patients with AD and MCI.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT02016560 and NCT03901105.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Comment in
-
Beyond the AJR: "Aggregated Tau Measured by Visual Interpretation of Flortaucipir Positron Emission Tomography and the Associated Risk of Clinical Progression of Mild Cognitive Impairment and Alzheimer Disease: Results From 2 Phase III Clinical Trials".AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2022 Jan;218(1):192. doi: 10.2214/AJR.21.26174. Epub 2021 May 12. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2022. PMID: 33978461 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

