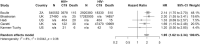Risk of adverse coronavirus disease 2019 outcomes for people living with HIV
- PMID: 33587448
- PMCID: PMC7924978
- DOI: 10.1097/QAD.0000000000002836
Risk of adverse coronavirus disease 2019 outcomes for people living with HIV
Abstract
Objective: To assess whether people living with HIV (PLWH) are at increased risk of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) mortality or adverse outcomes, and whether antiretroviral therapy (ART) influences this risk.
Design: Rapid review with meta-analysis and narrative synthesis.
Methods: We searched databases including Embase, Medline, medRxiv and Google Scholar up to 26 August 2020 for studies describing COVID-19 outcomes in PLWH and conducted a meta-analysis of higher quality studies.
Results: We identified 1908 studies and included 19 in the review. In a meta-analysis of five studies, PLWH had a higher risk of COVID-19 mortality [hazard ratio 1.95, 95% confidence interval (CI): 1.62-2.34] compared with people without HIV. Risk of death remained elevated for PLWH in a subgroup analysis of hospitalized cohorts (hazard ratio 1.60, 95% CI: 1.12-2.27) and studies of PLWH across all settings (hazard ratio 2.08, 95% CI: 1.69-2.56). Eight other studies assessed the association between HIV and COVID-19 outcomes, but provided inconclusive, lower quality evidence due to potential confounding and selection bias. There were insufficient data on the effect of CD4+ T-cell count and HIV viral load on COVID-19 outcomes. Eleven studies reported COVID-19 outcomes by ART-regimen. In the two largest studies, tenofovir disoproxil fumarate-based regimens were associated with a lower risk of adverse COVID-19 outcomes, although these analyses are susceptible to confounding by co-morbidities.
Conclusion: Emerging evidence suggests a moderately increased risk of COVID-19 mortality among PLWH. Further investigation into the relationship between COVID-19 outcomes and CD4+ T-cell count, HIV viral load, ART and the use of tenofovir disoproxil fumarate is warranted.
Copyright © 2021 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Comment in
-
An updated meta-analysis on the association between HIV infection and COVID-19 mortality.AIDS. 2021 Sep 1;35(11):1875-1878. doi: 10.1097/QAD.0000000000002968. AIDS. 2021. PMID: 34397487 No abstract available.
References
-
- World Health Organization (WHO). Weekly operational update on COVID-19, 21 August 2020. 2020; Geneva: World Health Organization (WHO), Available at: https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/weekly-update-on-covid-19---21-a.... [Accessed 18 January 2021].
-
- World Health Organization. HIV/AIDS fact sheet. 2020; Geneva: World Health Organization, Available at: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hiv-aids. [Accessed 18 January 2021].
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials