Antibiotic Adjuvant Activity Revealed in a Photoaffinity Approach to Determine the Molecular Target of Antipyocyanin Compounds
- PMID: 33587590
- PMCID: PMC8325921
- DOI: 10.1021/acsinfecdis.0c00160
Antibiotic Adjuvant Activity Revealed in a Photoaffinity Approach to Determine the Molecular Target of Antipyocyanin Compounds
Abstract
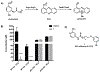
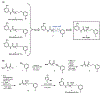
Infections with Pseudomonas aeruginosa are a looming threat to public health. New treatment strategies are needed to combat this pathogen, for example, by blocking the production of virulence factors like pyocyanin. A photoaffinity analogue of an antipyocyanin compound was developed to interrogate the inhibitor's molecular mechanism of action. While we sought to develop antivirulence inhibitors, the proteomics results suggested that the compounds had antibiotic adjuvant activity. Unexpectedly, we found that these compounds amplify the bactericidal activity of colistin, a well-characterized antibiotic, suggesting they may represent a first-in-class antibiotic adjuvant therapy. Analogues have the potential not only to widen the therapeutic index of cationic antimicrobial peptides like colistin, but also to be effective against colistin-resistant strains, strengthening our arsenal to combat P. aeruginosa infections.
Keywords: ArnA; PA14_30820; Pseudomonas aeruginosa; adjuvant; colistin.
Figures

References
-
- Breidenstein EB; de la Fuente-Nunez C; Hancock RE, Pseudomonas aeruginosa: all roads lead to resistance. Trends Microbiol. 2011, 19, 419–426. - PubMed
-
- CDC Antibiotic Resistance Threats in the United States; U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control: Atlanta, GA, 2019.
-
- WHO Global priority list of antibiotic-resistant bacteria to guide research, discovery, and development of new antibiotics; World Health Organization: Geneva, 2017.
-
- Zhou F; Yu T; Du R; Fan G; Liu Y; Liu Z; Xiang J; Wang Y; Song B; Gu X; Guan L; Wei Y; Li H; Wu X; Xu J; Tu S; Zhang Y; Chen H; Cao B, Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study. Lancet 2020, 395, 1054–1062. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

