Derivatization with 2-hydrazino-1-methylpyridine enhances sensitivity of analysis of 5α-dihydrotestosterone in human plasma by liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry
- PMID: 33588275
- PMCID: PMC7938423
- DOI: 10.1016/j.chroma.2021.461933
Derivatization with 2-hydrazino-1-methylpyridine enhances sensitivity of analysis of 5α-dihydrotestosterone in human plasma by liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry
Abstract
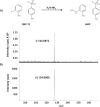
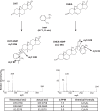
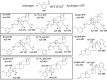
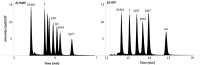
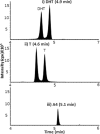
Liquid Chromatography tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) is the gold-standard approach for androgen analysis in biological fluids, superseding immunoassays in selectivity, particularly at low concentrations. While LC-MS/MS is established for analysis of testosterone and androstenedione, 5α-dihydrotestosterone (DHT) presents greater analytical challenges. DHT circulates at low nanomolar concentrations in men and lower in women, ionizing inefficiently and suffering from isobaric interference from other androgens. Even using current LC-MS/MS technology, large plasma volumes (>0.5 mL) are required for detection, undesirable clinically and unsuitable for animals. This study investigated derivatization approaches using hydrazine-based reagents to enhance ionization efficiency and sensitivity of analysis of DHT by LC-MS/MS. Derivatization of DHT using 2-hydrazino-1-methylpyridine (HMP) and 2-hydrazino-4-(trifluoromethyl)-pyrimidine (HTP) were compared. A method was validated using an UHPLC interfaced by electrospray with a triple quadruple mass spectrometer , analyzing human plasma (male and post-menopausal women) following solid-phase extraction. HMP derivatives were selected for validation affording greater sensitivity than those formed with HTP. HMP derivatives were detected by selected reaction monitoring (DHT-HMP m/z 396→108; testosterone-HMP m/z 394→108; androstenedione-HMP m/z 392→108). Chromatographic separation of androgen derivatives was optimized, carefully separating isobaric interferents and acceptable outputs for precision and trueness achieved following injection of 0.4 pg on column (approximately 34 pmol/L). HMP derivatives of all androgens tested could be detected in low plasma volumes: male (100 µL) and post-menopausal female (200 µL), and derivatives were stable over 30 days at -20°C. In conclusion, HMP derivatization, in conjunction with LC-MS/MS, is suitable for quantitative analysis of DHT, testosterone and androstenedione in low plasma volumes, offering advantages in sensitivity over current methodologies.
Keywords: 5α-Dihydrotestosterone; Androstenedione; Derivatization; Liquid chromatography mass spectrometry; Testosterone.
Copyright © 2021. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
2-hydrazino-1-methylpyridine: a highly sensitive derivatization reagent for oxosteroids in liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry.J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2005 Oct 25;825(2):214-22. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2004.12.007. Epub 2004 Dec 23. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2005. PMID: 16213450
-
Determination of prostatic androgens in 10 mg of tissue using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry with charged derivatization.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2005 Jun;382(4):1035-43. doi: 10.1007/s00216-005-3233-1. Epub 2005 May 21. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2005. PMID: 15909188
-
A direct assay for the routine measurement of testosterone, androstenedione, dihydrotestosterone and dehydroepiandrosterone by liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry.Ann Clin Biochem. 2016 Sep;53(Pt 5):580-7. doi: 10.1177/0004563215621096. Epub 2015 Nov 20. Ann Clin Biochem. 2016. PMID: 26589631
-
Androgen glucuronides analysis by liquid chromatography tandem-mass spectrometry: could it raise new perspectives in the diagnostic field of hormone-dependent malignancies?J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2013 Dec 1;940:24-34. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2013.09.022. Epub 2013 Sep 27. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2013. PMID: 24140653 Review.
-
Analysis of estrogens and androgens in postmenopausal serum and plasma by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry.Steroids. 2015 Jul;99(Pt A):76-83. doi: 10.1016/j.steroids.2014.08.012. Epub 2014 Aug 20. Steroids. 2015. PMID: 25150018 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Cold-induced phase separation for the simple and reliable extraction of sex hormones for subsequent LC-MS/MS analysis.J Lipid Res. 2022 Jan;63(1):100158. doi: 10.1016/j.jlr.2021.100158. Epub 2021 Dec 2. J Lipid Res. 2022. PMID: 34863861 Free PMC article.
-
Cyanoacetohydrazide as a Novel Derivatization Agent for the Determination of UHPLC-HRMS Steroids in Urine.Molecules. 2024 May 22;29(11):2433. doi: 10.3390/molecules29112433. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38893309 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid Analysis of Estrogens in Meat Samples by High Performance Liquid Chromatography with Fluorescence Detection.J Fluoresc. 2024 Jan;34(1):425-436. doi: 10.1007/s10895-023-03248-6. Epub 2023 Jun 7. J Fluoresc. 2024. PMID: 37284963
References
-
- Kratz A., Lewandrowski K.B. Case records of the Massachusetts General Hospital. Weekly clinicopathological exercises. Normal reference laboratory values. N. Engl. J. Med. 1998;339:1063–1072. - PubMed
-
- Kulle A.E., Riepe F.G., Melchior D., Hiort O., Holterhus P.M. A novel ultrapressure liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry method for the simultaneous determination of androstenedione, testosterone, and dihydrotestosterone in pediatric blood samples: age- and sex-specific reference data. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2010;95:2399–2409. - PubMed
-
- Rosner W., Vesper H. Toward excellence in testosterone testing: a consensus statement. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2010;95:4542–4548. - PubMed
-
- Vesper H.W., Botelho J.C. Standardization of testosterone measurements in humans. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2010;121:513–519. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

