Research Note: Increased myostatin expression and decreased expression of myogenic regulatory factors in embryonic ages in a quail line with muscle hypoplasia
- PMID: 33588344
- PMCID: PMC7896188
- DOI: 10.1016/j.psj.2021.01.001
Research Note: Increased myostatin expression and decreased expression of myogenic regulatory factors in embryonic ages in a quail line with muscle hypoplasia
Abstract
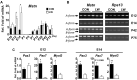
Genetic selection of quail for a low body weight for more than 80 generations established a low-weight (LW) Japanese quail line that has been previously characterized to have a muscle hypoplasia phenotype. The aim of this study is to investigate the relationship of temporal expression levels of myostatin (Mstn) and myogenic regulatory factors (MRFs) with hypoplastic muscle growth in the LW line. During embryonic day (E) 13 to 15, gain of embryo weight was 2-fold lower (P < 0.001) in the LW line than that in the random bred control (CON). Gains in body weight and pectoralis muscle weight from hatch to posthatch day (P) 28 were also significantly lower (P < 0.01) in the LW line but increased by 4-fold (P < 0.05) during P42 to P75. PCR analysis showed that expression levels of Mstn were greater in the LW at embryonic stage (E12 to E14, P < 0.05), but there was no difference after hatch. In addition, expression levels of Pax7 and myogenin (MyoG) at E12 were 23-fold (P < 0.05) and 3.4-fold (P < 0.05) lesser in the LW line, respectively. At E14, expression of Pax3, Pax7, and MyoG gene was 3.5-fold (P < 0.05), 6.5-fold (P = 0.065), and 4.4-fold (P < 0.01) less than that in the CON. Taken together, high expression levels of Mstn and low expression of MRFs during embryonic stages can be associated with development of muscle hypoplasia and delayed muscle growth in the LW quail line. These data provide evidence that genetic selection for a low body weight resulting in an avian model with muscle hypoplasia has altered the expression profiles of myogenic factors.
Keywords: muscle development; myofiber number; myogenic regulatory factor; myostatin; quail.
Copyright © 2021 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Research Note: Association of temporal expression of myostatin with hypertrophic muscle growth in different Japanese quail lines.Poult Sci. 2020 Jun;99(6):2926-2930. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2019.12.069. Epub 2020 Mar 19. Poult Sci. 2020. PMID: 32475426 Free PMC article.
-
Muscle hypertrophy in heavy weight Japanese quail line: delayed muscle maturation and continued muscle growth with prolonged upregulation of myogenic regulatory factors.Poult Sci. 2014 Sep;93(9):2271-7. doi: 10.3382/ps.2013-03844. Epub 2014 Jul 10. Poult Sci. 2014. PMID: 25012852
-
Skeletal muscle characterization of Japanese quail line selectively bred for lower body weight as an avian model of delayed muscle growth with hypoplasia.PLoS One. 2014 Apr 24;9(4):e95932. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0095932. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24763754 Free PMC article.
-
Mutations in the myostatin gene leading to hypermuscularity in mammals: indications for a similar mechanism in fish?Anim Genet. 2011 Jun;42(3):229-34. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2052.2010.02144.x. Epub 2010 Dec 22. Anim Genet. 2011. PMID: 21175702 Review.
-
The myogenic regulatory factors, determinants of muscle development, cell identity and regeneration.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2017 Dec;72:10-18. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2017.11.010. Epub 2017 Nov 15. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2017. PMID: 29127045 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Research Note: Growth promoting potential in Mstn mutant quail dependent and independent of increased egg size.Poult Sci. 2023 Jan;102(1):102260. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2022.102260. Epub 2022 Oct 18. Poult Sci. 2023. PMID: 36370661 Free PMC article.
-
Differential expression patterns of genes associated with metabolisms, muscle growth and repair in Pectoralis major muscles of fast- and medium-growing chickens.PLoS One. 2022 Oct 3;17(10):e0275160. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0275160. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 36190974 Free PMC article.
-
Developmental Characteristics of Skeletal Muscle during the Embryonic Stage in Chinese Yellow Quail (Coturnix japonica).Animals (Basel). 2023 Jul 14;13(14):2317. doi: 10.3390/ani13142317. Animals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37508093 Free PMC article.
-
Myostatin gene role in regulating traits of poultry species for potential industrial applications.J Anim Sci Biotechnol. 2024 Jun 3;15(1):82. doi: 10.1186/s40104-024-01040-5. J Anim Sci Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38825693 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A review of myostatin gene mutations: Enhancing meat production and potential in livestock genetic selection.Open Vet J. 2024 Dec;14(12):3189-3202. doi: 10.5455/OVJ.2024.v14.i12.4. Epub 2024 Dec 31. Open Vet J. 2024. PMID: 39927343 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Amirouche A., Durieux A.C., Banzet S., Koulmann N., Bonnefoy R., Mouret C., Bigard X., Peinnequin A., Freyssenet D. Down-regulation of Akt/mammalian target of rapamycin signaling pathway in response to myostatin overexpression in skeletal muscle. Endocrinology. 2009;150:286–294. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

