Circ SMARCA5 Inhibited Tumor Metastasis by Interacting with SND1 and Downregulating the YWHAB Gene in Cervical Cancer
- PMID: 33588586
- PMCID: PMC7894587
- DOI: 10.1177/0963689720983786
Circ SMARCA5 Inhibited Tumor Metastasis by Interacting with SND1 and Downregulating the YWHAB Gene in Cervical Cancer
Abstract
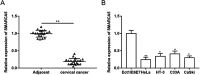
Cervical cancer is one of the diseases that seriously endanger women's health. Circular RNA plays an important role in regulating the occurrence and development of cervical cancer. Here, we investigated the mechanisms of circ SMARCA5 in the development of cervical cancer. Quantitative reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) results showed that the expression of SMARCA5 was downregulated in cervical cancer tissues and cell lines. Then we found that overexpression of SMARCA5 inhibited proliferation and invasion, but promoted apoptosis in cervical cancer cells. These were detected by Cell Counting Kit-8, Transwell, and Annexin V-fluorescein isothiocyanate/propidium iodide detection kit, respectively, and the expression of the apoptosis-related proteins was determined by western blotting. Then we predicted that SMARCA5 combined with Staphylococcal nuclease domain-containing 1 (SND1) by starBase, and verified by RNA pull-down assay. To further reveal the molecular mechanisms of SMARCA5 in the progression of cervical cancer, the interaction protein of SND1 was predicted by STRING, and the interaction was verified by co-immunoprecipitation assay. Then, the effects of SND1 or YWHAB on the development of cervical cancer were detected by the gain and loss function test, and we found that knockdown of SND1 or YWHAB reversed the effects of SMARCA5 short interfering RNA on proliferation, invasion, and apoptosis of cervical cancer cells. Overexpression of SMARCA5 inhibited cervical cancer metastasis in vivo. Our results showed that overexpression of circ SMARCA5 inhibits the binding of SND1 to YWHAB, and inhibits the proliferation and invasion, but promotes apoptosis in cervical cancer cells, thus inhibiting the metastasis of cervical cancer.
Keywords: Circ SMARCA5; SND1; YWHAB; cervical cancer; tumor metastasis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures







Similar articles
-
Hsa_circ_0031288/hsa-miR-139-3p/Bcl-6 regulatory feedback circuit influences the invasion and migration of cervical cancer HeLa cells.J Cell Biochem. 2020 Oct;121(10):4251-4260. doi: 10.1002/jcb.29650. Epub 2020 Apr 10. J Cell Biochem. 2020. PMID: 32277518
-
SND1 facilitates the invasion and migration of cervical cancer cells by Smurf1-mediated degradation of FOXA2.Exp Cell Res. 2020 Mar 1;388(1):111809. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2019.111809. Epub 2019 Dec 28. Exp Cell Res. 2020. PMID: 31891682
-
CircRNA VPRBP inhibits tumorigenicity of cervical cancer via miR-93-5p/FRMD6 axis.Reprod Sci. 2022 Aug;29(8):2251-2264. doi: 10.1007/s43032-022-00923-0. Epub 2022 May 2. Reprod Sci. 2022. PMID: 35501594
-
SND1-SMARCA5 interaction strengthened by PIM promotes the proliferation, metastasis, and chemoresistance of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.Int J Biol Macromol. 2025 Feb;291:139152. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.139152. Epub 2024 Dec 24. Int J Biol Macromol. 2025. PMID: 39725102
-
Hsa_circ_0001583 fuels bladder cancer metastasis by promoting staphylococcal nuclease and tudor domain containing 1-mediated MicroRNA decay.Neoplasia. 2024 Jan;47:100963. doi: 10.1016/j.neo.2023.100963. Epub 2024 Jan 3. Neoplasia. 2024. PMID: 38176295 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
YWHAB knockdown inhibits cell proliferation whilst promoting cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in colon cancer cells through PIK3R2.Exp Ther Med. 2023 Mar 17;25(5):193. doi: 10.3892/etm.2023.11892. eCollection 2023 May. Exp Ther Med. 2023. PMID: 37090079 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms and therapeutic implications of gene expression regulation by circRNA-protein interactions in cancer.Commun Biol. 2025 Jan 17;8(1):77. doi: 10.1038/s42003-024-07383-z. Commun Biol. 2025. PMID: 39825074 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hsa_circ_0009910 knockdown in HeLa cells increases miR‑198 expression levels and decreases c‑Met expression levels and cell viability.Oncol Lett. 2024 Nov 26;29(2):74. doi: 10.3892/ol.2024.14820. eCollection 2025 Feb. Oncol Lett. 2024. PMID: 39650233 Free PMC article.
-
Curcumenol Targeting YWHAG Inhibits the Pentose Phosphate Pathway and Enhances Antitumor Effects of Cisplatin.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022 Jun 26;2022:3988916. doi: 10.1155/2022/3988916. eCollection 2022. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022. PMID: 35795276 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNAs, long non-coding RNAs, and circular RNAs and gynecological cancers: focus on metastasis.Front Oncol. 2023 Oct 3;13:1215194. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1215194. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37854681 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

