Glutamate NMDA Receptor Antagonists with Relevance to Schizophrenia: A Review of Zebrafish Behavioral Studies
- PMID: 33588731
- PMCID: PMC9608229
- DOI: 10.2174/1570159X19666210215121428
Glutamate NMDA Receptor Antagonists with Relevance to Schizophrenia: A Review of Zebrafish Behavioral Studies
Abstract
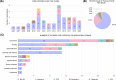
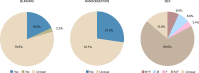
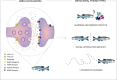
Schizophrenia pathophysiology is associated with hypofunction of glutamate NMDA receptors (NMDAR) in GABAergic interneurons and dopaminergic hyperactivation in subcortical brain areas. The administration of NMDAR antagonists is used as an animal model that replicates behavioral phenotypes relevant to the positive, negative, and cognitive symptoms of schizophrenia. Such models overwhelmingly rely on rodents, which may lead to species-specific biases and poor translatability. Zebrafish, however, is increasingly used as a model organism to study evolutionarily conserved aspects of behavior. We thus aimed to review and integrate the major findings reported in the zebrafish literature regarding the behavioral effects of NMDAR antagonists with relevance to schizophrenia. We identified 44 research articles that met our inclusion criteria from 590 studies retrieved from MEDLINE (PubMed) and Web of Science databases. Dizocilpine (MK-801) and ketamine were employed in 29 and 10 studies, respectively. The use of other NMDAR antagonists, such as phencyclidine (PCP), APV, memantine, and tiletamine, was described in 6 studies. Frequently reported findings are the social interaction and memory deficits induced by MK-801 and circling behavior induced by ketamine. However, mixed results were described for several locomotor and exploratory parameters in the novel tank and open tank tests. The present review integrates the most relevant results while discussing variation in experimental design and methodological procedures. We conclude that zebrafish is a suitable model organism to study drug-induced behavioral phenotypes relevant to schizophrenia. However, more studies are necessary to further characterize the major differences in behavior as compared to mammals.
Keywords: MK-801; PCP; Schizophrenia; behavior; glutamate antagonists; ketamine; psychosis; zebrafish.
Copyright© Bentham Science Publishers; For any queries, please email at epub@benthamscience.net.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

