Low expression of NSD1, NSD2, and NSD3 define a subset of human papillomavirus-positive oral squamous carcinomas with unfavorable prognosis
- PMID: 33588906
- PMCID: PMC7885607
- DOI: 10.1186/s13027-021-00347-6
Low expression of NSD1, NSD2, and NSD3 define a subset of human papillomavirus-positive oral squamous carcinomas with unfavorable prognosis
Abstract
Background: Frequent mutations in the nuclear receptor binding SET domain protein 1 (NSD1) gene have been observed in head and neck squamous cell carcinomas (HNSCC). NSD1 encodes a histone 3 lysine-36 methyltransferase. NSD1 mutations are correlated with improved clinical outcomes and increased sensitivity to platinum-based chemotherapy agents in human papillomavirus-negative (HPV-) tumors, despite weak T-cell infiltration. However, the role of NSD1 and related family members NSD2 and NSD3 in human papillomavirus-positive (HPV+) HNSCC is unclear.
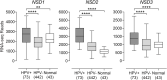
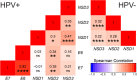
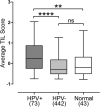
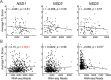
Methods: Using data from over 500 HNSCC patients from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA), we compared the relative level of mRNA expression of NSD1, NSD2, and NSD3 in HPV+ and HPV- HNSCC. Correlation analyses were performed between T-cell infiltration and the relative level of expression of NSD1, NSD2, and NSD3 mRNA in HPV+ and HPV- HNSCC. In addition, overall survival outcomes were compared for both the HPV+ and HPV- subsets of patients based on stratification by NSD1, NSD2, and NSD3 expression levels.
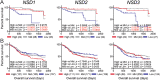
Results: Expression levels of NSD1, NSD2 or NSD3 were not correlated with altered lymphocyte infiltration in HPV+ HNSCC. More importantly, low expression of NSD1, NSD2, or NSD3 correlated with significantly reduced overall patient survival in HPV+, but not HPV- HNSCC.
Conclusion: These results starkly illustrate the contrast in molecular features between HPV+ and HPV- HNSCC tumors and suggest that NSD1, NSD2, and NSD3 expression levels should be further investigated as novel clinical metrics for improved prognostication and patient stratification in HPV+ HNSCC.
Keywords: Epigenetics; HPV; Head and neck cancer; Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma; Histone methyltransferase; The Cancer Genome Atlas; WHSC1; WHSC1L1.
Conflict of interest statement
The author reports no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
References
-
- Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68:394–424. - PubMed
-
- Hashibe M, Brennan P, Chuang S-C, et al. Interaction between tobacco and alcohol use and the risk of head and neck cancer: pooled analysis in the international head and neck Cancer epidemiology consortium. Cancer Epidemiol Biomark Prev. 2009;18:541–550. doi: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-08-0347. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

