Monitoring circulating dipeptidyl peptidase 3 (DPP3) predicts improvement of organ failure and survival in sepsis: a prospective observational multinational study
- PMID: 33588925
- PMCID: PMC7885215
- DOI: 10.1186/s13054-021-03471-2
Monitoring circulating dipeptidyl peptidase 3 (DPP3) predicts improvement of organ failure and survival in sepsis: a prospective observational multinational study
Abstract
Background: Dipeptidyl peptidase 3 (DPP3) is a cytosolic enzyme involved in the degradation of various cardiovascular and endorphin mediators. High levels of circulating DPP3 (cDPP3) indicate a high risk of organ dysfunction and mortality in cardiogenic shock patients.
Methods: The aim was to assess relationships between cDPP3 during the initial intensive care unit (ICU) stay and short-term outcome in the AdrenOSS-1, a prospective observational multinational study in twenty-four ICU centers in five countries. AdrenOSS-1 included 585 patients admitted to the ICU with severe sepsis or septic shock. The primary outcome was 28-day mortality. Secondary outcomes included organ failure as defined by the Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (SOFA) score, organ support with focus on vasopressor/inotropic use and need for renal replacement therapy. cDPP3 levels were measured upon admission and 24 h later.
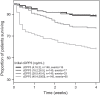
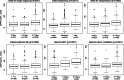
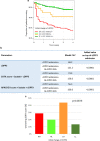
Results: Median [IQR] cDPP3 concentration upon admission was 26.5 [16.2-40.4] ng/mL. Initial SOFA score was 7 [5-10], and 28-day mortality was 22%. We found marked associations between cDPP3 upon ICU admission and 28-day mortality (unadjusted standardized HR 1.8 [CI 1.6-2.1]; adjusted HR 1.5 [CI 1.3-1.8]) and between cDPP3 levels and change in renal and liver SOFA score (p = 0.0077 and 0.0009, respectively). The higher the initial cDPP3 was, the greater the need for organ support and vasopressors upon admission; the longer the need for vasopressor(s), mechanical ventilation or RRT and the higher the need for fluid load (all p < 0.005). In patients with cDPP3 > 40.4 ng/mL upon admission, a decrease in cDPP3 below 40.4 ng/mL after 24 h was associated with an improvement of organ function at 48 h and better 28-day outcome. By contrast, persistently elevated cDPP3 at 24 h was associated with worsening organ function and high 28-day mortality.
Conclusions: Admission levels and rapid changes in cDPP3 predict outcome during sepsis. Trial Registration ClinicalTrials.gov, NCT02393781. Registered on March 19, 2015.
Keywords: Biomarker; DPP3; Organ dysfunction; Outcome; Sepsis; Septic shock.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors have reviewed and approved the manuscript and are willing to attest to their qualifications as authors, disclose potential conflicts of interest, and release copyright should the manuscript be accepted for publication.
Dr. Mebazaa reports personal fees from Orion, Servier, Otsuka, Philips, Sanofi, Adrenomed, Epygon and Fire 1 and grants and personal fees from 4TEEN4, Abbott and Sphingotec. BD and ABl were invited to meetings in Hennigsdorf by 4TEEN4 Pharmaceuticals GmbH. KS and ABe are employees of 4TEEN4 Pharmaceuticals GmbH. BC served as a member of an advisory board for Roche Diagnostic. ML reports research support from sphingotec, lecture fees from Baxter and Fresenius, consulting fees from Novartis. Other authors declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research authorship and/or publication of this article. 4TEEN4 Pharmaceuticals GmbH holds patent rights on the DPP3 biomarker and humanized antibody Procizumab. This does not alter our adherence to Critical Care Medicine policies on sharing data and materials.
Figures

References
-
- Prajapati SC, Chauhan SS. Human dipeptidyl peptidase III mRNA variant I and II are expressed concurrently in multiple tumor derived cell lines and translated at comparable efficiency in vitro. MolBiol Rep. 2016;43:457–462. - PubMed
-
- Pang X, Shimizu A, Kurita S, Zankov DP, Takeuchi K, Yasuda-Yamahara M, et al. Novel therapeutic role for dipeptidyl peptidase III in the treatment of hypertension. Hypertens Dallas Tex. 1979;2016(68):630–641. - PubMed
-
- Deniau B, Rehfeld L, Santos K, Dienelt A, Azibani F, Sadoune M, et al. Circulating dipeptidyl peptidase 3 is a myocardial depressant factor: dipeptidyl peptidase 3 inhibition rapidly and sustainably improves haemodynamics. Eur J Heart Fail. 2019; - PubMed
-
- Takagi K, Blet A, Levy B, Deniau B, Azibani F, Feliot E, et al. Circulating dipeptidyl peptidase 3 and alteration in haemodynamics in cardiogenic shock: results from the OptimaCC trial. Eur J Heart Fail. 2019; - PubMed
-
- Dépret F, Amzallag J, Pollina A, Fayolle-Pivot L, Coutrot M, Chaussard M, et al. Circulating dipeptidyl peptidase-3 at admission is associated with circulatory failure, acute kidney injury and death in severely ill burn patients. Crit Care LondEngl. 2020;24:168. doi: 10.1186/s13054-020-02888-5. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

