Anti-Mesothelin CAR T cell therapy for malignant mesothelioma
- PMID: 33588928
- PMCID: PMC7885509
- DOI: 10.1186/s40364-021-00264-1
Anti-Mesothelin CAR T cell therapy for malignant mesothelioma
Abstract
Malignant mesothelioma (MM) is a treatment-resistant tumor originating in the mesothelial lining of the pleura or the abdominal cavity with very limited treatment options. More effective therapeutic approaches are urgently needed to improve the poor prognosis of MM patients. Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR) T cell therapy has emerged as a novel potential treatment for this incurable solid tumor. The tumor-associated antigen mesothelin (MSLN) is an attractive target for cell therapy in MM, as this antigen is expressed at high levels in the diseased pleura or peritoneum in the majority of MM patients and not (or very modestly) present in healthy tissues. Clinical trials using anti-MSLN CAR T cells in MM have shown that this potential therapeutic is relatively safe. However, efficacy remains modest, likely due to the MM tumor microenvironment (TME), which creates strong immunosuppressive conditions and thus reduces anti-MSLN CAR T cell tumor infiltration, efficacy and persistence. Various approaches to overcome these challenges are reviewed here. They include local (intratumoral) delivery of anti-MSLN CAR T cells, improved CAR design and co-stimulation, and measures to avoid T cell exhaustion. Combination therapies with checkpoint inhibitors as well as oncolytic viruses are also discussed. Preclinical studies have confirmed that increased efficacy of anti-MSLN CAR T cells is within reach and offer hope that this form of cellular immunotherapy may soon improve the prognosis of MM patients.
Keywords: CAR T cells; Cancer; Immunotherapy; Malignant mesothelioma; Malignant pleural mesothelioma; Mesothelin; Tumor microenvironment.
Conflict of interest statement
LC, DY and NvZ declare that they have no competing interests.
JEJR reports advisory roles as chair of Gene Technology Technical Advisory committee, and in the Office of the Gene Technology Regulator, and Australian Government. JEJR also reports honoraria speaker fees or advisory roles for GSK, Takeda, Gilead, Cynata, Pfizer, Spark, Novartis, Celgene, bluebird bio, Shire, Avrobio; stocks in Genea; consultant role for Rarecyte (stocks in lieu) and Imago.
Figures

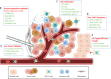
References
-
- Henderson DW, Reid G, Kao SC, van Zandwijk N, Klebe S. Challenges and controversies in the diagnosis of mesothelioma: part 1. Cytology-only diagnosis, biopsies, immunohistochemistry, discrimination between mesothelioma and reactive mesothelial hyperplasia, and biomarkers. J Clin Pathol. 2013;66(10):847–853. doi: 10.1136/jclinpath-2012-201303. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Husain AN, Colby T, Ordonez N, Krausz T, Attanoos R, Beasley MB, et al. Guidelines for pathologic diagnosis of malignant mesothelioma: 2012 update of the consensus statement from the international mesothelioma interest group. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2012;137(5):647–667. doi: 10.5858/arpa.2012-0214-OA. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

