Real world effectiveness and tolerability of candesartan in the treatment of migraine: a retrospective cohort study
- PMID: 33589682
- PMCID: PMC7884682
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-83508-2
Real world effectiveness and tolerability of candesartan in the treatment of migraine: a retrospective cohort study
Abstract
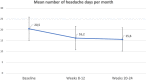
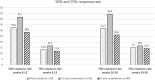
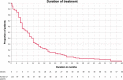
To date, two randomized, controlled studies support the use of candesartan for migraine prophylaxis but with limited external validity. We aim to evaluate the effectiveness and tolerability of candesartan in clinical practice and to explore predictors of patient response. Retrospective cohort study including all patients with migraine who received candesartan between April 2008-February 2019. The primary endpoint was the number of monthly headache days during weeks 8-12 of treatment compared to baseline. Additionally, we evaluated the frequency during weeks 20-24. We analysed the percentage of patients with 50% and 75% response rates and the retention rates after three and 6 months of treatment. 120/4121 patients were eligible, aged 45.9 [11.5]; 100 (83.3%) female. Eighty-four patients (70%) had chronic migraine and 53 (42.7%) had medication-overuse headache. The median number of prior prophylactics was 3 (Inter-quartile range 2-5). At baseline, patients had 20.5 ± 8.5 headache days per month, decreasing 4.3 ± 8.4 days by 3 months (weeks 12-16) and by 4.7 ± 8.7 days by 6 months (paired Student's t-test, p < 0.001). The percentage of patients with a 50% response was 32.5% at 3 months and 31.7% at 6 months, while the retention rate was 85.0% and 58.3%. The number of prior treatments (Odds ratio 0.79, 95% CI 0.64-0.97) and the presence of daily headache (Odds ratio 0.39, 95% CI 0.16-0.97) were associated with a lower probability of response. Candesartan showed beneficial effects in the preventive treatment of migraine in clinical practice, including patients with chronic migraine, medication-overuse headache and resistance to prior prophylactics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
CandeSpartan Study: Candesartan Spanish Response-prediction and Tolerability study in migraine.Cephalalgia. 2024 Apr;44(4):3331024241248833. doi: 10.1177/03331024241248833. Cephalalgia. 2024. PMID: 38663908
-
Candesartan in migraine prevention: results from a retrospective real-world study.J Neurol. 2020 Nov;267(11):3243-3247. doi: 10.1007/s00415-020-09989-9. Epub 2020 Jun 15. J Neurol. 2020. PMID: 32542525
-
Prophylactic treatment of migraine with an angiotensin II receptor blocker: a randomized controlled trial.JAMA. 2003 Jan 1;289(1):65-9. doi: 10.1001/jama.289.1.65. JAMA. 2003. PMID: 12503978 Clinical Trial.
-
Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers for the prevention of migraines.Ann Pharmacother. 2010 Feb;44(2):360-6. doi: 10.1345/aph.1M312. Epub 2010 Jan 19. Ann Pharmacother. 2010. PMID: 20086184 Review.
-
Candesartan cilexetil: in children and adolescents aged 1 to <17 years with hypertension.Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 2010;10(5):335-42. doi: 10.2165/11206300-000000000-00000. Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 2010. PMID: 20860416 Review.
Cited by
-
Phenotype of new daily persistent headache: subtypes and comparison to transformed chronic daily headache.J Headache Pain. 2023 Aug 16;24(1):109. doi: 10.1186/s10194-023-01639-5. J Headache Pain. 2023. PMID: 37587430 Free PMC article.
-
Migraine: from pathophysiology to treatment.J Neurol. 2023 Jul;270(7):3654-3666. doi: 10.1007/s00415-023-11706-1. Epub 2023 Apr 8. J Neurol. 2023. PMID: 37029836 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Renin Angiotensin System as a Therapeutic Target in Traumatic Brain Injury.Neurotherapeutics. 2023 Oct;20(6):1565-1591. doi: 10.1007/s13311-023-01435-8. Epub 2023 Sep 27. Neurotherapeutics. 2023. PMID: 37759139 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pharmacogenetics in Primary Headache Disorders.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Feb 10;12:820214. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.820214. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35222013 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Combining treatments for migraine prophylaxis: the state-of-the-art.J Headache Pain. 2024 Dec 5;25(1):214. doi: 10.1186/s10194-024-01925-w. J Headache Pain. 2024. PMID: 39639191 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ogihara T, Higashimori K, Masuo K, Mikami H. Pilot study of a new angiontensin II receptor antagonist, TCV-116: effects of a single dose on blood pressure in patients with essential hypertension. Clin. Ther. 1993;15(4):684–191. - PubMed
-
- Stovner LJ, Linde M, Gravdahl GB, Tronvik E, Aamodt AH, Sand T, et al. A comparative study of candesartan versus propranolol for migraine prophylaxis: a randomised, triple-blind, placebo-controlled, double cross-over study. Cephalalgia. 2014;34(7):523–532. doi: 10.1177/0333102413515348. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

