Activation-induced cytidine deaminase is a possible regulator of cross-talk between oocytes and granulosa cells through GDF-9 and SCF feedback system
- PMID: 33589683
- PMCID: PMC7884688
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-83529-x
Activation-induced cytidine deaminase is a possible regulator of cross-talk between oocytes and granulosa cells through GDF-9 and SCF feedback system
Abstract
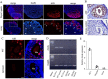
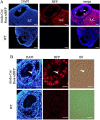
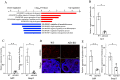
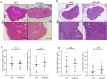
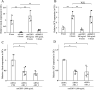
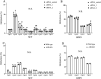
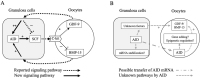
Activation-induced cytidine deaminase (AID, Aicda) is a master gene regulating class switching of immunoglobulin genes. In this study, we investigated the significance of AID expression in the ovary. Immunohistological study and RT-PCR showed that AID was expressed in murine granulosa cells and oocytes. However, using the Aicda-Cre/Rosa-tdRFP reporter mouse, its transcriptional history in oocytes was not detected, suggesting that AID mRNA in oocytes has an exogenous origin. Microarray and qPCR validation revealed that mRNA expressions of growth differentiation factor-9 (GDF-9) in oocytes and stem cell factor (SCF) in granulosa cells were significantly decreased in AID-knockout mice compared with wild-type mice. A 6-h incubation of primary granuloma cells markedly reduced AID expression, whereas it was maintained by recombinant GDF-9. In contrast, SCF expression was induced by more than threefold, whereas GDF-9 completely inhibited its increase. In the presence of GDF-9, knockdown of AID by siRNA further decreased SCF expression. However, in AID-suppressed granulosa cells and ovarian tissues of AID-knockout mice, there were no differences in the methylation of SCF and GDF-9. These findings suggest that AID is a novel candidate that regulates cross-talk between oocytes and granulosa cells through a GDF-9 and SCF feedback system, probably in a methylation-independent manner.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Growth differentiation factor-9 is expressed by the primate follicle throughout the periovulatory interval.Biol Reprod. 2003 Aug;69(2):725-32. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod.103.015891. Epub 2003 Apr 16. Biol Reprod. 2003. PMID: 12700191
-
Regulatory role of kit ligand-c-kit interaction and oocyte factors in steroidogenesis by rat granulosa cells.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2012 Jul 6;358(1):18-26. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2012.02.011. Epub 2012 Feb 24. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2012. PMID: 22366471
-
Comparison of recombinant growth differentiation factor-9 and oocyte regulation of KIT ligand messenger ribonucleic acid expression in mouse ovarian follicles.Biol Reprod. 2000 Dec;63(6):1669-75. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod63.6.1669. Biol Reprod. 2000. PMID: 11090434
-
Stem cell factor (SCF)-kit mediated phosphatidylinositol 3 (PI3) kinase signaling during mammalian oocyte growth and early follicular development.Front Biosci. 2006 Jan 1;11:126-35. doi: 10.2741/1785. Front Biosci. 2006. PMID: 16146719 Review.
-
GDF-9 and BMP-15 direct the follicle symphony.J Assist Reprod Genet. 2018 Oct;35(10):1741-1750. doi: 10.1007/s10815-018-1268-4. Epub 2018 Jul 23. J Assist Reprod Genet. 2018. PMID: 30039232 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Uterine Deletion of Bmal1 Impairs Placental Vascularization and Induces Intrauterine Fetal Death in Mice.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jul 11;23(14):7637. doi: 10.3390/ijms23147637. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35886985 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

