A MALDI-TOF MS database for fast identification of Vibrio spp. potentially pathogenic to marine mollusks
- PMID: 33590268
- PMCID: PMC7954726
- DOI: 10.1007/s00253-021-11141-0
A MALDI-TOF MS database for fast identification of Vibrio spp. potentially pathogenic to marine mollusks
Abstract
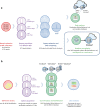
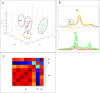
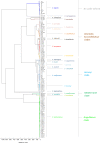
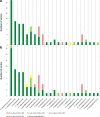
In mollusk aquaculture, a large number of Vibrio species are considered major pathogens. Conventional methods based on DNA amplification and sequencing used to accurately identify Vibrio species are unsuitable for monitoring programs because they are time-consuming and expensive. The aim of this study was, therefore, to develop the MALDI-TOF MS method in order to establish a rapid identification technique for a large panel of Vibrio species. We created the EnviBase containing 120 main spectra projections (MSP) of the Vibrio species that are potentially responsible for mollusk diseases, comprising 25 species: V. aestuarianus, V. cortegadensis, V. tapetis and species belonging to the Coralliilyticus, Harveyi, Mediterranei, and Orientalis clades. Each MSP was constructed by the merger of raw spectra obtained from three different media and generated by three collaborating laboratories to increase the diversity of the conditions and thus obtain a good technique robustness. Perfect discrimination was obtained with all of the MSP created for the Vibrio species and even for very closely related species as V. europaeus and V. bivalvicida. The new EnviBase library was validated through a blind test on 100 Vibrio strains performed by our three collaborators who used the direct transfer and protein extraction methods. The majority of the Vibrio strains were successfully identified with the newly created EnviBase by the three laboratories for both protocol methods. This study documents the first development of a freely accessible database exclusively devoted to Vibrio found in marine environments, taking into account the high diversity of this genus. KEY POINTS: • Development of a MALDI-TOF MS database to quickly affiliate Vibrio species. • Increase of the reactivity when faced with Vibrio associated with mollusk diseases. • Validation of MALDI-TOF MS as routine diagnostic tool.
Keywords: Database; MALDI-TOF MS; Marine mollusk pathogens; Vibrio.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Al-Saari N, Gao F, Rohul AAKM, Sato K, Sato K, Mino S, Suda W, Oshima K, Hattori M, Ohkuma M, Meirelles PM, Thompson FL, Thompson C, Filho GMA, Gomez-Gil B, Sawabe T, Sawabe T. Advanced microbial taxonomy combined with genome-based-approaches reveals that Vibrio astriarenae sp nov., an agarolytic marine bacterium, forms a new clade in Vibrionaceae. PLoS One. 2015;10(8):e0136279. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0136279. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Arnold RJ, Reilly JP. Fingerprint matching of E. coli strains with matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry of whole cells using a modified correlation approach. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 1998;12:630–636. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0231(19980529)12:10<630::AID-RCM206>3.0.CO;2-0. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Azevedo C, Conchas RF, Montes J. Description of Haplosporidium edule n. sp. (Phylum Haplosporidia), a parasite of Cerastoderma edule (Mollusca, Bivalvia) with complex spore ornamentation. Eur J Protistol. 2003;39(2):161–167. doi: 10.1078/0932-4739-00905. - DOI
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

