Hyperpolarized 13 C Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Fumarate Metabolism by Parahydrogen-induced Polarization: A Proof-of-Concept in vivo Study
- PMID: 33590933
- PMCID: PMC8251594
- DOI: 10.1002/cphc.202001038
Hyperpolarized 13 C Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Fumarate Metabolism by Parahydrogen-induced Polarization: A Proof-of-Concept in vivo Study
Abstract
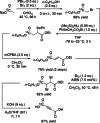
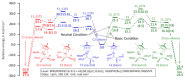
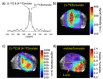
Hyperpolarized [1-13 C]fumarate is a promising magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) biomarker for cellular necrosis, which plays an important role in various disease and cancerous pathological processes. To demonstrate the feasibility of MRI of [1-13 C]fumarate metabolism using parahydrogen-induced polarization (PHIP), a low-cost alternative to dissolution dynamic nuclear polarization (dDNP), a cost-effective and high-yield synthetic pathway of hydrogenation precursor [1-13 C]acetylenedicarboxylate (ADC) was developed. The trans-selectivity of the hydrogenation reaction of ADC using a ruthenium-based catalyst was elucidated employing density functional theory (DFT) simulations. A simple PHIP set-up was used to generate hyperpolarized [1-13 C]fumarate at sufficient 13 C polarization for ex vivo detection of hyperpolarized 13 C malate metabolized from fumarate in murine liver tissue homogenates, and in vivo 13 C MR spectroscopy and imaging in a murine model of acetaminophen-induced hepatitis.
Keywords: density functional calculations; fumarate; hyperpolarized 13C MRS/I; matabolism; parahydrogen-induced polarization.
© 2021 The Authors. ChemPhysChem published by Wiley-VCH GmbH.
Figures



References
-
- Neves A. A., Brindle K. M., J. Nucl. Med. 2014, 55, 1–4. - PubMed
-
- Reshef A., Shirvan A., Akselrod-Ballin A., Wall A., Ziv I., J. Nucl. Med. 2010, 51, 837–840. - PubMed
-
- Kurhanewicz J., Vigneron D. B., Ardenkjaer-Larsen J. H., Bankson J. A., Brindle K., Cunningham C. H., Gallagher F. A., Keshari K. R., Kjaer A., Laustsen C., Mankoff D. A., Merritt M. E., Nelson S. J., Pauly J. M., Lee P., Ronen S., Tyler D. J., Rajan S. S., Spielman D. M., Wald L., Zhang X., Malloy C. R., Rizi R., Neoplasia. 2019, 21, 1–16. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

