Successful improved peripheral tissue perfusion was seen in patients with atherosclerosis after 12 months of treatment with aged garlic extract
- PMID: 33590955
- PMCID: PMC8450802
- DOI: 10.1111/iwj.13570
Successful improved peripheral tissue perfusion was seen in patients with atherosclerosis after 12 months of treatment with aged garlic extract
Abstract
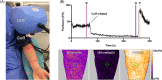
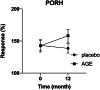
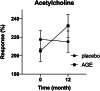
Patients with arteriolosclerosis have impaired microvascular perfusion leading to impaired wound healing. Aged garlic extract has shown to have a positive impact on vascular elasticity. The present study aimed to assess the effect of long-term treatment with AGE on peripheral tissue perfusion in patients with confirmed atherosclerosis. Ninety three patients with a CT-scan confirmed coronary artery arteriolosclerosis were randomised in a double-blind manner to placebo or 2400 mg AGE daily for 1 year. Peripheral tissue perfusion was evaluated at 0- and 12-months using Laser Speckle Contrast Imaging. Measurement of post occlusive reactive hyperemia (PORH) and cutaneous vascular conductance (CVC) using acetylcholine iontophoresis (Ach) was conducted. After 12 months a significant increase of 21.6% (95% CI 3.2%-40.0%, P < .05) was seen in the relative change of PORH in the AGE compared with the placebo group. The same response was seen for CVC and Ach with an increase of 21.4% (95% CI 3.4%-39.4%, P < .05) in the AGE group compared with the placebo group. Aged garlic extract regenerated peripheral tissue perfusion and increase microcirculation in patients with arteriolosclerosis. Adequate peripheral tissue perfusion and tissue oxygen tension are important prerequisites for successful tissue repair. Restored microcirculation in patients could hypothetically facilitate wound healing.
Keywords: aged garlic extract; atherosclerosis; double blinded; laser speckle contrast imaging; peripheral tissue perfusion.
© 2021 The Authors. International Wound Journal published by Medicalhelplines.com Inc (3M) and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr Lindstedt has received a grant to support this research from Wakunaga of America LTD. None of the other authors has conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Aged garlic extract preserves cutaneous microcirculation in patients with increased risk for cardiovascular diseases: A double-blinded placebo-controlled study.Int Wound J. 2019 Dec;16(6):1487-1493. doi: 10.1111/iwj.13220. Epub 2019 Sep 13. Int Wound J. 2019. PMID: 31518044 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Comparison of laser speckle contrast imaging with laser Doppler for assessing microvascular function.Microvasc Res. 2011 Nov;82(3):326-32. doi: 10.1016/j.mvr.2011.07.007. Epub 2011 Jul 22. Microvasc Res. 2011. PMID: 21803051
-
Acute effects of coffee on skin blood flow and microvascular function.Microvasc Res. 2017 Nov;114:58-64. doi: 10.1016/j.mvr.2017.06.006. Epub 2017 Jun 15. Microvasc Res. 2017. PMID: 28625890 Clinical Trial.
-
Assessment of endothelial and neurovascular function in human skin microcirculation.Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2013 Jul;34(7):373-84. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2013.05.007. Epub 2013 Jun 21. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2013. PMID: 23791036 Review.
-
Current Methods to Assess Human Cutaneous Blood Flow: An Updated Focus on Laser-Based-Techniques.Microcirculation. 2016 Jul;23(5):337-44. doi: 10.1111/micc.12257. Microcirculation. 2016. PMID: 26607042 Review.
Cited by
-
A review on the effect of garlic on diabetes, BDNF, and VEGF as a potential treatment for diabetic retinopathy.Chin Med. 2023 Feb 17;18(1):18. doi: 10.1186/s13020-023-00725-9. Chin Med. 2023. PMID: 36803536 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Heart-brain interaction in cardiogenic dementia: pathophysiology and therapeutic potential.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024 Jan 24;11:1304864. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2024.1304864. eCollection 2024. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024. PMID: 38327496 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of aged garlic extract on aging?related changes in gastrointestinal function and enteric nervous system cells.Exp Ther Med. 2025 Mar 26;29(5):103. doi: 10.3892/etm.2025.12853. eCollection 2025 May. Exp Ther Med. 2025. PMID: 40171138 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying atheroprotective fruits and vegetables by Mendelian Randomization analysis.Front Nutr. 2024 Oct 14;11:1426763. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1426763. eCollection 2024. Front Nutr. 2024. PMID: 39469330 Free PMC article.
-
Aged Garlic Extract Reduces IL-6: A Double-Blind Placebo-Controlled Trial in Females with a Low Risk of Cardiovascular Disease.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021 Mar 31;2021:6636875. doi: 10.1155/2021/6636875. eCollection 2021. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021. PMID: 33868439 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Leys D. Atherothrombosis: a major health burden. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2001;11(Suppl 2):1‐4. - PubMed
-
- Glass CK, Witztum JL. Atherosclerosis: the road ahead. Cell. 2001;104(4):503‐516. - PubMed
-
- Levy BI, Schiffrin EL, Mourad JJ, et al. Impaired tissue perfusion: a pathology common to hypertension, obesity, and diabetes mellitus. Circulation. 2008;118(9):968‐976. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

