Proximity proteomics in a marine diatom reveals a putative cell surface-to-chloroplast iron trafficking pathway
- PMID: 33591270
- PMCID: PMC7972479
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.52770
Proximity proteomics in a marine diatom reveals a putative cell surface-to-chloroplast iron trafficking pathway
Abstract
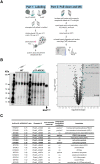
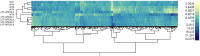
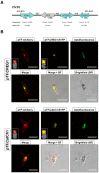
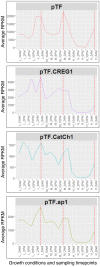
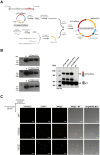
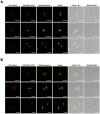
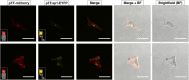
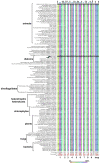
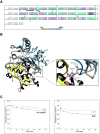
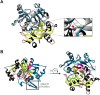
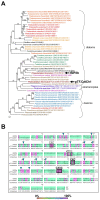
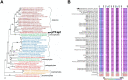
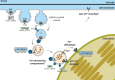
Iron is a biochemically critical metal cofactor in enzymes involved in photosynthesis, cellular respiration, nitrate assimilation, nitrogen fixation, and reactive oxygen species defense. Marine microeukaryotes have evolved a phytotransferrin-based iron uptake system to cope with iron scarcity, a major factor limiting primary productivity in the global ocean. Diatom phytotransferrin is endocytosed; however, proteins downstream of this environmentally ubiquitous iron receptor are unknown. We applied engineered ascorbate peroxidase APEX2-based subcellular proteomics to catalog proximal proteins of phytotransferrin in the model marine diatom Phaeodactylum tricornutum. Proteins encoded by poorly characterized iron-sensitive genes were identified including three that are expressed from a chromosomal gene cluster. Two of them showed unambiguous colocalization with phytotransferrin adjacent to the chloroplast. Further phylogenetic, domain, and biochemical analyses suggest their involvement in intracellular iron processing. Proximity proteomics holds enormous potential to glean new insights into iron acquisition pathways and beyond in these evolutionarily, ecologically, and biotechnologically important microalgae.
Keywords: APEX2; chloroplast; diatom; infectious disease; iron; metal trafficking; microbiology; phytotransferrin; plant biology.
© 2021, Turnšek et al.
Conflict of interest statement
JT, JB, MV, TD, AH, MO, VB, AA No competing interests declared
Figures





References
-
- Aguirre JD, Clark HM, McIlvin M, Vazquez C, Palmere SL, Grab DJ, Seshu J, Hart PJ, Saito M, Culotta VC. A manganese-rich environment supports superoxide dismutase activity in a lyme disease pathogen, Borrelia burgdorferi. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2013;288:8468–8478. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.433540. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

