Pathomechanisms and therapeutic opportunities in radiation-induced heart disease: from bench to bedside
- PMID: 33591377
- PMCID: PMC8055626
- DOI: 10.1007/s00392-021-01809-y
Pathomechanisms and therapeutic opportunities in radiation-induced heart disease: from bench to bedside
Abstract
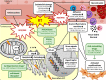
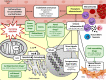
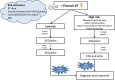
Cancer management has undergone significant improvements, which led to increased long-term survival rates among cancer patients. Radiotherapy (RT) has an important role in the treatment of thoracic tumors, including breast, lung, and esophageal cancer, or Hodgkin's lymphoma. RT aims to kill tumor cells; however, it may have deleterious side effects on the surrounding normal tissues. The syndrome of unwanted cardiovascular adverse effects of thoracic RT is termed radiation-induced heart disease (RIHD), and the risk of developing RIHD is a critical concern in current oncology practice. Premature ischemic heart disease, cardiomyopathy, heart failure, valve abnormalities, and electrical conduct defects are common forms of RIHD. The underlying mechanisms of RIHD are still not entirely clear, and specific therapeutic interventions are missing. In this review, we focus on the molecular pathomechanisms of acute and chronic RIHD and propose preventive measures and possible pharmacological strategies to minimize the burden of RIHD.
Keywords: Molecular pathomechanisms of radiation-induced heart disease; Onco-cardiology; Prevention and therapy of radiation-induced heart disease; Radiation heart sequelae.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures

References
-
- WHO. Cardiovascular Diseases (CVDs) (2017). Available from: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs317/en/
-
- WHO. Cancer (2018). Available from: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/cancer
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- FK129094/Hungarian Scientific Research Fund
- GINOP-2.3.2-15-2016-00040/Nemzeti Kutatási Fejlesztési és Innovációs Hivatal
- EFOP-3.6.2-16-2017-00006 (LIVE LONGER)/Nemzeti Kutatási Fejlesztési és Innovációs Hivatal
- ÚNKP-20-5-SZTE-166/Emberi Eroforrások Minisztériuma
- ÚNKP-20-4-SZTE-150/Emberi Eroforrások Minisztériuma
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

