Cross-species identification of PIP5K1-, splicing- and ubiquitin-related pathways as potential targets for RB1-deficient cells
- PMID: 33591981
- PMCID: PMC7909629
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1009354
Cross-species identification of PIP5K1-, splicing- and ubiquitin-related pathways as potential targets for RB1-deficient cells
Abstract
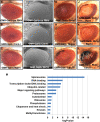
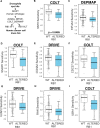
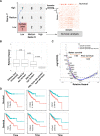
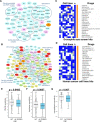
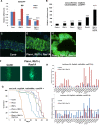
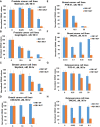
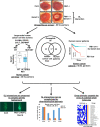
The RB1 tumor suppressor is recurrently mutated in a variety of cancers including retinoblastomas, small cell lung cancers, triple-negative breast cancers, prostate cancers, and osteosarcomas. Finding new synthetic lethal (SL) interactions with RB1 could lead to new approaches to treating cancers with inactivated RB1. We identified 95 SL partners of RB1 based on a Drosophila screen for genetic modifiers of the eye phenotype caused by defects in the RB1 ortholog, Rbf1. We validated 38 mammalian orthologs of Rbf1 modifiers as RB1 SL partners in human cancer cell lines with defective RB1 alleles. We further show that for many of the RB1 SL genes validated in human cancer cell lines, low activity of the SL gene in human tumors, when concurrent with low levels of RB1 was associated with improved patient survival. We investigated higher order combinatorial gene interactions by creating a novel Drosophila cancer model with co-occurring Rbf1, Pten and Ras mutations, and found that targeting RB1 SL genes in this background suppressed the dramatic tumor growth and rescued fly survival whilst having minimal effects on wild-type cells. Finally, we found that drugs targeting the identified RB1 interacting genes/pathways, such as UNC3230, PYR-41, TAK-243, isoginkgetin, madrasin, and celastrol also elicit SL in human cancer cell lines. In summary, we identified several high confidence, evolutionarily conserved, novel targets for RB1-deficient cells that may be further adapted for the treatment of human cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Evidence for autoregulation and cell signaling pathway regulation from genome-wide binding of the Drosophila retinoblastoma protein.G3 (Bethesda). 2012 Nov;2(11):1459-72. doi: 10.1534/g3.112.004424. Epub 2012 Nov 1. G3 (Bethesda). 2012. PMID: 23173097 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted Inhibition of the E3 Ligase SCFSkp2/Cks1 Has Antitumor Activity in RB1-Deficient Human and Mouse Small-Cell Lung Cancer.Cancer Res. 2020 Jun 1;80(11):2355-2367. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-19-2400. Epub 2020 Apr 7. Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 32265224 Free PMC article.
-
Paradoxical instability-activity relationship defines a novel regulatory pathway for retinoblastoma proteins.Mol Biol Cell. 2010 Nov 15;21(22):3890-901. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E10-06-0520. Epub 2010 Sep 22. Mol Biol Cell. 2010. PMID: 20861300 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted pharmacologic inhibition of S-phase kinase-associated protein 2 (SKP2) mediated cell cycle regulation in lung and other RB-Related cancers: A brief review of current status and future prospects.Adv Biol Regul. 2023 May;88:100964. doi: 10.1016/j.jbior.2023.100964. Epub 2023 Mar 14. Adv Biol Regul. 2023. PMID: 37004354 Review.
-
Regulation of cancer metabolism by oncogenes and tumor suppressors.Methods Enzymol. 2014;542:59-80. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-416618-9.00003-0. Methods Enzymol. 2014. PMID: 24862260 Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting phosphoinositide signaling in cancer: relevant techniques to study lipids and novel avenues for therapeutic intervention.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023 Oct 25;11:1297355. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1297355. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 37954209 Free PMC article.
-
Synthetic lethality prediction in DNA damage repair, chromatin remodeling and the cell cycle using multi-omics data from cell lines and patients.Sci Rep. 2023 Apr 29;13(1):7049. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-34161-4. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37120674 Free PMC article.
-
Tissue-specific modulation of NADH consumption as an anti-aging intervention in Drosophila.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Jan 6:2025.01.06.631511. doi: 10.1101/2025.01.06.631511. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 39829793 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Combinatorial interventions in aging.Nat Aging. 2023 Oct;3(10):1187-1200. doi: 10.1038/s43587-023-00489-9. Epub 2023 Oct 2. Nat Aging. 2023. PMID: 37783817 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intratumor HIF-1α modulates production of a cachectic ligand to cause host wasting.Cell Insight. 2025 Apr 8;4(3):100247. doi: 10.1016/j.cellin.2025.100247. eCollection 2025 Jun. Cell Insight. 2025. PMID: 40336592 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

