A common binding motif in the ET domain of BRD3 forms polymorphic structural interfaces with host and viral proteins
- PMID: 33592170
- PMCID: PMC8349776
- DOI: 10.1016/j.str.2021.01.010
A common binding motif in the ET domain of BRD3 forms polymorphic structural interfaces with host and viral proteins
Abstract
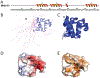
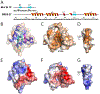
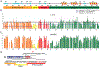
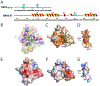
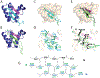
The extraterminal (ET) domain of BRD3 is conserved among BET proteins (BRD2, BRD3, BRD4), interacting with multiple host and viral protein-protein networks. Solution NMR structures of complexes formed between the BRD3 ET domain and either the 79-residue murine leukemia virus integrase (IN) C-terminal domain (IN329-408) or its 22-residue IN tail peptide (IN386-407) alone reveal similar intermolecular three-stranded β-sheet formations. 15N relaxation studies reveal a 10-residue linker region (IN379-388) tethering the SH3 domain (IN329-378) to the ET-binding motif (IN389-405):ET complex. This linker has restricted flexibility, affecting its potential range of orientations in the IN:nucleosome complex. The complex of the ET-binding peptide of the host NSD3 protein (NSD3148-184) and the BRD3 ET domain includes a similar three-stranded β-sheet interaction, but the orientation of the β hairpin is flipped compared with the two IN:ET complexes. These studies expand our understanding of molecular recognition polymorphism in complexes of ET-binding motifs with viral and host proteins.
Keywords: BET proteins; BRD3; Moloney murine leukemia virus; NSD3; extraterminal domain; integrase; interdomain dynamics; isotope peptide labeling; solution NMR.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests G.T.M. is a founder of Nexomics Biosciences, Inc. G.L. is chief scientific officer and director of Nexomics Biosciences, Inc. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Comment in
-
A tail goes viral by forming an anchor and a tether.Structure. 2021 Aug 5;29(8):783-786. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2021.07.004. Structure. 2021. PMID: 34358464
References
-
- AIYER S, SWAPNA GV, MALANI N, ARAMINI JM, SCHNEIDER WM, PLUMB MR, GHANEM M, LARUE RC, SHARMA A, STUDAMIRE B, KVARATSKHELIA M, BUSHMAN FD, MONTELIONE GT & ROTH MJ 2014. Altering murine leukemia virus integration through disruption of the integrase and BET protein family interaction. Nucleic Acids Res, 42, 5917–28. - PMC - PubMed
-
- BARAN MC, HUANG YJ, MOSELEY HN & MONTELIONE GT 2004. Automated analysis of protein NMR assignments and structures. Chem Rev, 104, 3541–56. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

