Panbio™ rapid antigen test for SARS-CoV-2 has acceptable accuracy in symptomatic patients in primary health care
- PMID: 33592253
- PMCID: PMC7881288
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jinf.2021.02.014
Panbio™ rapid antigen test for SARS-CoV-2 has acceptable accuracy in symptomatic patients in primary health care
Abstract
Objectives: We aimed to evaluate the accuracy of the Panbio™ Ag-RDT at primary health care (PHC) centers and test sites in symptomatic patients and close contacts, using the Reverse-Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR) test as the gold standard.
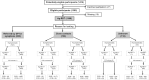
Methods: The study was conducted in four PHC centers and two test sites in Mallorca, Spain. Consecutive patients older than 18 years, attending the sites for RT-PCR testing were included. Two nasopharyngeal samples were collected, one for RT-PCR and the other was processed on-site using the Panbio™ rapid antigen test kit for SARS-CoV-2. The sensitivity and specificity were calculated using RT-PCR as the reference, and the predictive values using the pretest probability results for each analyzed group.
Findings: A total of 1369 participants were included; mean age 42.5 ± 14.9 years and 54.3% women. The overall prevalence was 10.2%. Most participants (70.6%) presented within 5 days of the onset of symptoms. The overall sensitivity was of 71.4% (95% CI: 63.1%, 78.7%), the specificity of 99.8% (95% CI: 99.4%, 99.9%), the positive predictive value of 98.0% (95% CI: 93.0%, 99.7%) and a negative predictive value of 96.8% (95% CI: 95.7%, 97.7%). The sensitivity was higher in symptomatic patients, in those arriving within 5 days since symptom onset and in those with high viral load.
Interpretation: Ag-RDT had relatively good performance characteristics in suspected symptomatic patients within five days since the onset of symptoms. However, our data do not support the sole use of Panbio™ Ag-RDT in asymptomatic individuals.
Funding: None.
Keywords: COVID-19; Primary care; Rapid antigen test; Sar-CoV-2.
Copyright © 2021. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declared no conflict of interest.
Figures
Comment in
-
Rapid antigen test for SARS-CoV-2 and primary health care.J Infect. 2021 Aug;83(2):237-279. doi: 10.1016/j.jinf.2021.05.001. Epub 2021 May 8. J Infect. 2021. PMID: 33971208 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Rapid Risk Assessment: increased transmission of COVID-19 in the EU/EEA and the UK – thirteenth update [Internet]. 2020 [cited 2020 Nov 6]. Available from: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/publications-data/covid-19-risk-assessment...
-
- World Health Organization. Antigen-detection in the diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 infection using rapid immunoassays. 2020 [cited 2020 Sep 18];369 (6508):1167–8. Available from: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/antigen-detection-in-the-diagnos...
-
- Center for Disease Control and Prevention. Interim Guidance for Rapid Antigen Testing for SARS-CoV-2 CDC. 2020; Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/lab/resources/antigen-tests-gu...
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous