An incomplete form of anti-ganglioside antibody-positive Miller Fisher syndrome after an Epstein-Barr virus infection: A case report
- PMID: 33592894
- PMCID: PMC7870176
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000024451
An incomplete form of anti-ganglioside antibody-positive Miller Fisher syndrome after an Epstein-Barr virus infection: A case report
Abstract
Rationale: The Miller Fisher syndrome (MFS) is an acute polyradiculoneuritis regarded as an uncommon clinical variant of the Guillain-Barre syndrome (GBS). It is characterized by the clinical triad of ophthalmoplegia, ataxia, and areflexia. The diagnosis of MFS is based on clinical presentation, presence of albuminocytologic dissociation in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), and normal brain imaging results. The presence of anti-ganglioside antibodies (GQlb) in the serum is helpful for the diagnosis. A history of upper respiratory tract infection or diarrhea 3 days to 6 weeks before the onset of MFS is common. However, there are some patients with atypical manifestations who are difficult to diagnose. Here, we present an incomplete form of MFS where antibodies against GQ1b were detected in the serum following an Epstein Barr virus (EBV) infection.
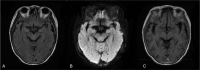
Patient concerns: A 77-year-old Chinese woman was admitted to the hospital with acute diplopia and right blepharoptosis. She had a history of mild upper respiratory tract infection 2 weeks ago. In 1 week, the symptoms rapidly progressed into bilateral ophthalmoplegia and hyporeflexia of the limbs without ataxia. CSF analysis on the third day after onset was normal, without albuminocytologic dissociation. EBV immunoglobulin G (IgG) antibodies were detected in the CSF. GQ1b and GD1b IgG antibodies were positive in the serum and negative in the CSF. No responsible lesion was found on brain imaging examination.
Diagnoses: In accordance with the progressive bilateral ophthalmoplegia and hyporeflexia, the history of upper respiratory tract infection, the detection of EBV and GQ1b antibodies, and the negative brain imaging examination, the diagnosis of MFS was confirmed.
Interventions: The patient was administered intravenous immunoglobulin for 5 days.
Outcomes: She had a favorable outcome after treatment. At the 6-week follow-up, bilateral ocular movement limitation and tendon reflexes had recovered.
Lessons: The diagnosis of MFS can be challenging, especially when encountered with incomplete symptoms and normal CSF results. Attention should be paid to the presence of anti-GQ1b IgG antibodies when the clinical manifestations are incomplete. Furthermore, EBV primary infection could be associated with MFS and considered a potential causative agent.
Copyright © 2021 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Anti-GQ1b IgG antibody syndrome: clinical and immunological range.J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2001 Jan;70(1):50-5. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.70.1.50. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2001. PMID: 11118247 Free PMC article.
-
Bickerstaff brainstem encephalitis-Miller-Fisher syndrome (BBE-MFS) overlap with negative anti-GQ1b serology.BMJ Case Rep. 2024 Dec 22;17(12):e261975. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2024-261975. BMJ Case Rep. 2024. PMID: 39950622
-
Anti-GQ1b antibody syndrome presenting as acute isolated bilateral ophthalmoplegia: Report on two patients and review of the literature.Eur J Paediatr Neurol. 2016 May;20(3):439-43. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpn.2016.02.002. Epub 2016 Feb 18. Eur J Paediatr Neurol. 2016. PMID: 26924168 Review.
-
Ocular Manifestations of Miller Fisher Syndrome: a Case Report.Med Arch. 2021 Jun;75(3):234-236. doi: 10.5455/medarh.2021.75.234-236. Med Arch. 2021. PMID: 34483456 Free PMC article.
-
Miller Fisher syndrome developing as a parainfectious manifestation of dengue fever: a case report and review of the literature.J Med Case Rep. 2019 May 2;13(1):120. doi: 10.1186/s13256-019-2066-z. J Med Case Rep. 2019. PMID: 31043165 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Neuromuscular Complications of SARS-CoV-2 and Other Viral Infections.Front Neurol. 2022 Jun 24;13:914411. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2022.914411. eCollection 2022. Front Neurol. 2022. PMID: 35812094 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Miller Fisher Syndrome Presenting Without Areflexia, Ophthalmoplegia, and Albuminocytological Dissociation: A Case Report.Cureus. 2022 Mar 21;14(3):e23371. doi: 10.7759/cureus.23371. eCollection 2022 Mar. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 35475055 Free PMC article.
-
Graves' disease with anti-GQ1b antibody syndrome: a rare case report.BMC Neurol. 2021 May 28;21(1):212. doi: 10.1186/s12883-021-02245-1. BMC Neurol. 2021. PMID: 34049504 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical and antibodies analysis of anti-GQ1b antibody syndrome: a case series of 15 patients.Acta Neurol Belg. 2023 Jun;123(3):839-847. doi: 10.1007/s13760-022-01940-1. Epub 2022 Apr 11. Acta Neurol Belg. 2023. PMID: 35399126 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Fisher M. An unusual variant of acute idiopathic polyneuritis (syndrome of ophthalmoplegia, ataxia and areflexia). N Engl J Med 1956;255:57–65. - PubMed
-
- Mori M, Kuwabara S, Fukutake T, et al. Clinical features and prognosis of Miller Fisher syndrome. Neurology 2001;56:1104–6. - PubMed
-
- Koga M, Gilbert M, Li J, et al. Antecedent infections in Fisher syndrome: a common pathogenesis of molecular mimicry. Neurology 2005;64:1605–11. - PubMed
-
- Hughes RA, Cornblath DR. Guillain-Barré syndrome. N Engl J Med 2012;366:2294–304. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

