PFKFB4 promotes lung adenocarcinoma progression via phosphorylating and activating transcriptional coactivator SRC-2
- PMID: 33593309
- PMCID: PMC7887818
- DOI: 10.1186/s12890-021-01420-x
PFKFB4 promotes lung adenocarcinoma progression via phosphorylating and activating transcriptional coactivator SRC-2
Abstract
Background: To investigate the role and its potential mechanism of 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase 4 (PFKFB4) in lung adenocarcinoma.
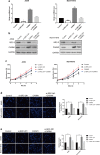
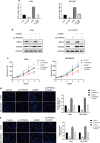
Methods: Co-immunoprecipitation was performed to analyze the interaction between PFKFB4 and SRC-2. Western blot was used to investigate the phosphorylation of steroid receptor coactivator-2 (SRC-2) on the condition that PFKFB4 was knockdown. Transcriptome sequencing was performed to find the downstream target of SRC-2. Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) assay, transwell assay and transwell-matrigel assay were used to examine the proliferation, migration and invasion abilities in A549 and NCI-H1975 cells with different treatment.
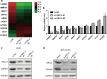
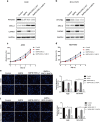
Results: In our study we found that PFKFB4 was overexpressed in lung adenocarcinoma associated with SRC family protein and had an interaction with SRC-2. PFKFB4 could phosphorylate SRC-2 at Ser487, which altered SRC-2 transcriptional activity. Functionally, PFKFB4 promoted lung adenocarcinoma cells proliferation, migration and invasion by phosphorylating SRC-2. Furthermore, we identified that CARM1 was transcriptionally regulated by SRC-2 and involved in PFKFB4-SRC-2 axis on lung adenocarcinoma progression.
Conclusions: Our research reveal that PFKFB4 promotes lung adenocarcinoma cells proliferation, migration and invasion via enhancing phosphorylated SRC-2-mediated CARM1 expression.
Keywords: Lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD); PFKFB4; Phosphorylation; SRC-2.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Metabolic enzyme PFKFB4 activates transcriptional coactivator SRC-3 to drive breast cancer.Nature. 2018 Apr;556(7700):249-254. doi: 10.1038/s41586-018-0018-1. Epub 2018 Apr 3. Nature. 2018. PMID: 29615789 Free PMC article.
-
miR-186-5p promotes cell growth, migration and invasion of lung adenocarcinoma by targeting PTEN.Exp Mol Pathol. 2019 Jun;108:105-113. doi: 10.1016/j.yexmp.2019.04.007. Epub 2019 Apr 11. Exp Mol Pathol. 2019. PMID: 30981721
-
KIF18B as a regulator in microtubule movement accelerates tumor progression and triggers poor outcome in lung adenocarcinoma.Tissue Cell. 2019 Dec;61:44-50. doi: 10.1016/j.tice.2019.09.001. Epub 2019 Sep 3. Tissue Cell. 2019. PMID: 31759406
-
LPCAT1 promotes brain metastasis of lung adenocarcinoma by up-regulating PI3K/AKT/MYC pathway.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019 Feb 21;38(1):95. doi: 10.1186/s13046-019-1092-4. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 30791942 Free PMC article.
-
ETV4 promotes proliferation and invasion of lung adenocarcinoma by transcriptionally upregulating MSI2.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2019 Aug 13;516(1):278-284. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2019.06.115. Epub 2019 Jun 25. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2019. PMID: 31253395
Cited by
-
Effect of PFKFB4 on the Prognosis and Immune Regulation of NSCLC and Its Mechanism.Int J Gen Med. 2022 Aug 2;15:6341-6353. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S369126. eCollection 2022. Int J Gen Med. 2022. PMID: 35942289 Free PMC article.
-
PFKFB4 facilitates palbociclib resistance in oestrogen receptor-positive breast cancer by enhancing stemness.Cell Prolif. 2023 Jan;56(1):e13337. doi: 10.1111/cpr.13337. Epub 2022 Sep 20. Cell Prolif. 2023. PMID: 36127291 Free PMC article.
-
Moonlighting functions of glucose metabolic enzymes and metabolites in cancer.Nat Rev Cancer. 2025 Jun;25(6):426-446. doi: 10.1038/s41568-025-00800-3. Epub 2025 Apr 2. Nat Rev Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40175621 Review.
-
THOC3 interacts with YBX1 to promote lung squamous cell carcinoma progression through PFKFB4 mRNA modification.Cell Death Dis. 2023 Jul 27;14(7):475. doi: 10.1038/s41419-023-06008-3. Cell Death Dis. 2023. PMID: 37500615 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel Hypoxia-Related Gene Signature with Strong Predicting Ability in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Identified by Comprehensive Profiling.Int J Genomics. 2022 May 19;2022:8594658. doi: 10.1155/2022/8594658. eCollection 2022. Int J Genomics. 2022. PMID: 35634481 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

