miRNAs as biomarkers for early cancer detection and their application in the development of new diagnostic tools
- PMID: 33593374
- PMCID: PMC7885381
- DOI: 10.1186/s12938-021-00857-9
miRNAs as biomarkers for early cancer detection and their application in the development of new diagnostic tools
Abstract
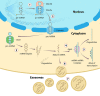
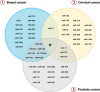
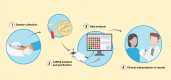
Over the last decades, microRNAs (miRNAs) have emerged as important molecules associated with the regulation of gene expression in humans and other organisms, expanding the strategies available to diagnose and handle several diseases. This paper presents a systematic review of literature of miRNAs related to cancer development and explores the main techniques used to quantify these molecules and their limitations as screening strategy. The bibliographic research was conducted using the online databases, PubMed, Google Scholar, Web of Science, and Science Direct searching the terms "microRNA detection", "miRNA detection", "miRNA and prostate cancer", "miRNA and cervical cancer", "miRNA and cervix cancer", "miRNA and breast cancer", and "miRNA and early cancer diagnosis". Along the systematic review over 26,000 published papers were reported, and 252 papers were returned after applying the inclusion and exclusion criteria, which were considered during this review. The aim of this study is to identify potential miRNAs related to cancer development that may be useful for early cancer diagnosis, notably in the breast, prostate, and cervical cancers. In addition, we suggest a preliminary top 20 miRNA panel according to their relevance during the respective cancer development. Considering the progressive number of new cancer cases every year worldwide, the development of new diagnostic tools is critical to refine the accuracy of screening tests, improving the life expectancy and allowing a better prognosis for the affected patients.
Keywords: Biomarkers; Breast cancer; Cervical cancer; Early cancer diagnosis; Liquid biopsies; MiRNA; Prostate cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

