A nomogram to predict the high-risk RS in HR+/HER2-breast cancer patients older than 50 years of age
- PMID: 33593381
- PMCID: PMC7885620
- DOI: 10.1186/s12967-021-02743-3
A nomogram to predict the high-risk RS in HR+/HER2-breast cancer patients older than 50 years of age
Abstract
Background: The 21-gene recurrence score (RS) testing can predict the prognosis for luminal breast cancer patients. Meanwhile, patients > 50 years with RS > 25 have improved survival with adjuvant chemotherapy. The current study aimed to develop a nomogram with routine parameters to predict RS.
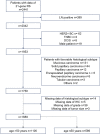
Methods: We included patients diagnosed with hormone receptor (HR)-positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor-2 (HER2)-negative who underwent the 21-gene RS testing and aged > 50 years. The primary outcome was high-risk RS (> 25). Univariate and multivariate analyses were performed to identify significant predictors. A predictive nomogram based on logistic model was developed and evaluated with receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves. The nomogram was internally validated for discrimination and calibration with bootstrapping method, and externally validated in another cohort. We then assessed the nomogram in different subgroups of patients and compared it with several published models.
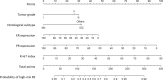
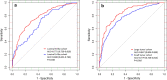
Results: A total of 1100 patients were included. Five clinicopathological parameters were used as predictors of a high-risk RS, including tumor grade, histologic subtype, ER expression, PR expression, and Ki-67 index. The area under the curve (AUC) was 0.798 (95% CI 0.772-0.825) and optimism adjusted AUC was 0.794 (95% CI 0.781-0.822). External validation demonstrated an AUC value of 0.746 (95% CI 0.685-0.807), which had no significant difference with the training cohort (P = 0.124). Calibration plots indicated that the nomogram-predicted results were well fitted to the actual outcomes in both internal and external validation. The nomogram had better discriminate ability in patients who had tumors > 2 cm (AUC = 0.847, 95% CI 0.804-0.890). When compared with four other existing models, similar AUC was observed between our nomogram and the model constructed by discriminate Lee et al. CONCLUSIONS: We developed a user-friendly nomogram to predict the high-risk RS in luminal breast cancer patients who were older than 50 years of age, which could guide treatment decision making for those who have no access to the 21-gene RS testing.
Keywords: Breast cancer; Nomogram; Predict; The 21-gene recurrence score.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Validation of CTS5 Model in Large-scale Breast Cancer Population and Combination of CTS5 and Ki-67 Status to Develop a Novel Nomogram for Prognosis Prediction.Am J Clin Oncol. 2024 May 1;47(5):228-238. doi: 10.1097/COC.0000000000001080. Epub 2023 Dec 22. Am J Clin Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38131531
-
Oncotype DX Predictive Nomogram for Recurrence Score Output: The Novel System ADAPTED01 Based on Quantitative Immunochemistry Analysis.Clin Breast Cancer. 2020 Oct;20(5):e600-e611. doi: 10.1016/j.clbc.2020.04.012. Epub 2020 May 5. Clin Breast Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32565110
-
Nomogram Update to Predict the High Genomic Risk Breast Cancer by Different Races.Clin Breast Cancer. 2024 Feb;24(2):e61-e70.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.clbc.2023.10.005. Epub 2023 Oct 22. Clin Breast Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38007348 Clinical Trial.
-
Development of a nomogram to predict recurrence scores obtained using Oncotype DX in Japanese patients with breast cancer.Breast Cancer. 2024 Nov;31(6):1018-1027. doi: 10.1007/s12282-024-01616-z. Epub 2024 Jul 17. Breast Cancer. 2024. PMID: 39020239 Free PMC article.
-
Is radiomic MRI a feasible alternative to OncotypeDX® recurrence score testing? A systematic review and meta-analysis.BJS Open. 2021 Sep 6;5(5):zrab081. doi: 10.1093/bjsopen/zrab081. BJS Open. 2021. PMID: 34633438 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
A Novel Surrogate Nomogram Capable of Predicting OncotypeDX Recurrence Score©.J Pers Med. 2022 Jul 8;12(7):1117. doi: 10.3390/jpm12071117. J Pers Med. 2022. PMID: 35887614 Free PMC article.
-
Prediction of the 70-gene signature (MammaPrint) high versus low risk by nomograms among axillary lymph node positive (LN+) and negative (LN-) Chinese breast cancer patients, a retrospective study.BMC Cancer. 2025 Jul 1;25(1):1128. doi: 10.1186/s12885-025-14507-z. BMC Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40597882 Free PMC article.
-
Nomogram prediction of the 70-gene signature (MammaPrint) binary and quartile categorized risk using medical history, imaging features and clinicopathological data among Chinese breast cancer patients.J Transl Med. 2023 Nov 9;21(1):798. doi: 10.1186/s12967-023-04523-7. J Transl Med. 2023. PMID: 37946210 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

